An Australian research group developed a novel open-source software to help stakeholders make cost-effective renewable energy investments. Dubbed CEREI, the software was designed for the regulatory environment of the Australian state of Victoria but can be tweaked to serve other regions.
“The tool's architecture is flexible, allowing it to be adapted and scaled up to accommodate different parameters and tariff models from other regions, enhancing its applicability in diverse energy markets and making it suitable for worldwide use,” said corresponding author Dr. Ibrahim Ibrahim, to pv magazine.
The program's user interface asks for seven input files with a resolution of 30 minutes. First, the users are asked to log the components of the network tariff, such as energy and network charges and local market charges. Secondly, they are asked to log energy usage data for the intended use, and in the third input, energy costs are given.
In the fourth input, the user uploads the forecasted energy generation from the on-site renewable energy source, whether PV, wind power, or other relevant source. In input five, the feed-in tariff is logged, while in input six, the user is asked to upload a summary of a reference energy bill for comparison. In the final seventh input, the user logs life cycle cost parameters, including capital cost, inflation rate, and degradation rate.
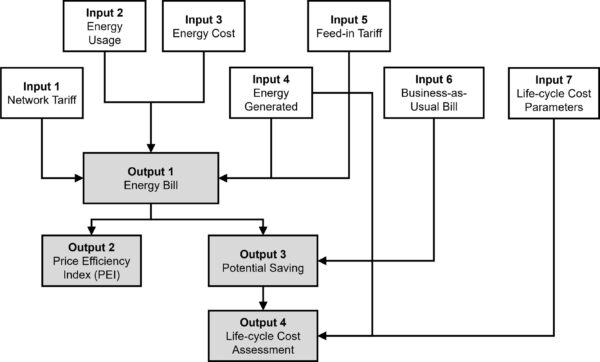
Image: University of Technology Sydney, SoftwareX, CC BY 4.0 DEED
With those inputs, the software can yield a few outputs. It can provide an estimated energy bill and potential savings as it compares it to the reference bill. In addition, it shows a price efficiency index (PEI) result for an entire year. Lastly, it offers a life cycle cost assessment, including a levelized cost of energy (LCOE), and a simple payback period. Furthermore, the tool can be used for behind-the-meter scenarios where some electricity is consumed and some is fed to the grid, as well as in scenarios in which the electricity is only sold to the grid.
Popular content
“The proposed tool can support industrial and commercial customers in Australia to reduce their electrical energy bills and the distribution of the on-site generation behind-the-meter,” said the scientists. “In addition, it can help decision-makers within industrial and commercial organizations to identify cost-effective renewable energy solutions and support the integration of renewable energy sources into existing power systems.”
The software was presented in the paper “CEREI: An open-source tool for Cost-Effective Renewable Energy Investments,” published in the journal SoftwareX. The CEREI software was developed by scientists from the University of Technology Sydney and the Federation University Australia.
“One of the notable strengths of CEREI is its ability to strike a balance between energy demand, generation, demand response, and wholesale balancing energy,” the academics concluded. “Moreover, by providing a comprehensive overview of various tariff structures and renewable energy investment alternatives, CEREI aids in simplifying complex decisions, making the path to a green energy future more accessible.”
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.

By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.