Tunisia launches 200 MW solar tender
Tunisia’s Ministry of Industry, Mines and Energy has kicked off a new procurement exercise for large-scale solar.
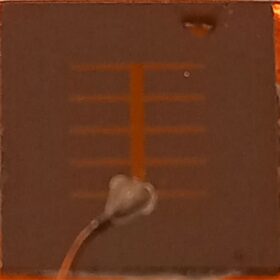
First attempt to build solar cells based on gallium phosphide, titanium
After conducting theoretical studies on gallium phosphide, titanium solar cells for years, a group of Spanish researchers has now sought to build the first intermediate band device based on this material combination and has found it can achieve enhanced external quantum efficiency at wavelengths above 550 nm.
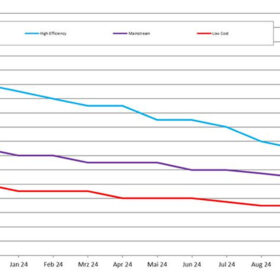
TOPCon solar panel prices falling in Germany amid industry struggles
Martin Schachinger, the founder of pvXchange.com, reports that tunnel oxide passivated contact (TOPCon) solar module prices in Germany have fallen by an average of €0.010 ($0.0109)/W this month. Demand remains especially weak in the residential sector, while complex authorization processes are also challenging the commercial and industrial (C&I) and ground-mounted segments.
Solving the UV problem of n-type solar
Laboratory testing has revealed that some negatively-doped, “n-type” tunnel oxide passivated contact (TOPCon) and heterojunction (HJT) solar modules are susceptible to ultraviolet (UV) light-related damage and degradation. That could mean trouble down the line, if modules in the field begin to show UV-related performance loss. Manufacturers are implementing solutions at cell and module level.
Chinese PV Industry Brief: Arctech secures 2.3 GW tracker order in Saudi Arabia
Arctech Solar says it has signed a 2.3 GW tracker order from Saudi Arabia, where it will supply trackers designed for the region’s desert terrain and high winds.
Indonesia’s installed solar capacity surpasses 700 MW
The Institute for Essential Services Reform says Indonesia’s solar industry has faced a downturn over the past two years, but policy reforms should accelerate solar deployment in the coming years. The think tank’s latest report states that 16.92 GW of projects are currently in the pipeline across the country.
Engie commissions 2.3 MW lightweight rooftop PV system in Belgium
Installed by Engie’s Sun4business subsidiary, the C&I project features solar PV panels from Dutch manufacturer Solarge that weigh just 7 kg/m2.
The Hydrogen Stream: US researchers explore trapped geologic hydrogen
US researchers have started studying hydrogen formation in the Midcontinent Rift in the United States, while Dutch scientists have discovered that hydrogen emissions from industrial complexes are higher than previously estimated.
BASF receives funding for world’s largest industrial heat pump
The German government has awarded a €310 million ($336 million) funding package to chemical manufacturer BASF for the construction of an industrial heat pump with a capacity of up to 500,000 metric tons of steam per year. It will use waste heat from steam crackers for CO2-free stream production.
General Motors launches residential storage system
The US-based automotive manufacturing company said its new storage system offers the option of integrating with PV systems. It can be scaled to reach a capacity of up to 35.4 kWh, which the company said would enable approximately 20 hours of storage.