Japan-based technology company Sharp Corporation offers a range of space-qualified compound solar cells for use in low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites and other spacecraft. It recently exhibited its space-grade PV devices at Space Tech Expo Europe 2025, a space industry trade show and conference held in Bremen, Germany.
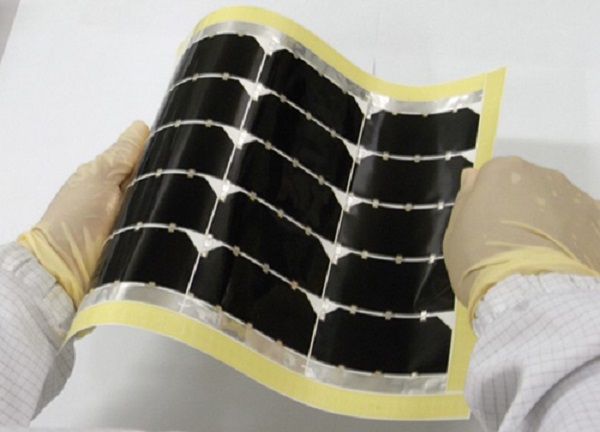
“The company has over five decades of space product development and research,” a spokesperson from Sharp told pv magazine. It is now offering a thin, sheet-type solar panel that encapsulates its high-efficiency compound triple-junction type cells for space applications.
Developed and manufactured by Sharp, such panels are lightweight and flexible but robust, suitable for mounting on curved surfaces, according to the company. The modules were used last year on the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) probe, which landed on the lunar surface in January 2024.
“Even after the lunar landing, the solar panel continued to supply power necessary for communication with Earth for several months, demonstrating reliable performance in harsh environments,” said the company in a statement.
Sharp also offers a glass sheet panel for its compound solar cells, made with protective radiation-resistant glass. The design is lightweight, offering “superior flexibility,” making it suitable for long-term missions, such as planetary exploration and deep space exploration.
A third variation is a cover glass integrated solar cell assembly, dubbed cell-interconnect-coverglass (CiC), which bonds the protective cover glass to each solar cell. It is based on Sharp’s “unique internal wiring technology” that enables the use of CiC with thin-film compound solar cells despite their thinness.
The company has a wide range of space-qualified cell technologies. Its standard inverted metamorphic triple junction space solar cells have a 31% efficiency. The standard triple-junction compound space cells are based on germanium (Ge) and have an efficiency of 28.7%. Its space-qualified silicon products have an efficiency of 17.4%.
Sharp also confirmed recent media reports about its plans to leverage its organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display manufacturing expertise in the development of perovskite solar PV products for a range of applications.
In February of this year, Sharp announced ahead of a PV Expo 2025 event in Japan that it was developing high-efficiency perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells for practical applications, such as “building roofs with limited installation space, mobile devices, cars, and powering digital signage.”
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.


By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.