All low-cost PV monitoring systems at a glance
A group of scientists in China conducted a comprehensive review of existing low-cost photovoltaic monitoring approaches. They found that only 11 out of 88 studies related to PV monitoring incorporate machine learning. The researchers urge the scientific community to place greater emphasis on lightweight machine learning solutions and smartphone-based integration.
Swiss researchers develop snow model to optimize PV system design in alpine regions
The researchers have used computational fluid dynamics-based modelling of snow patterns in an effort to establish best practices to mitigate snow accumulation in alpine PV plants.
From scale to strength: How India’s solar industry is forced to become a global premium player
EUPD Research explores India’s rapid solar manufacturing expansion, its growing export potential, competitiveness relative to China, and the evolving trade and sustainability dynamics shaping global PV markets.
Chinese solar cell prices ease as looming Indian antidumping duties prompt contract renegotiations
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, OPIS, a Dow Jones company, provides a quick look at the main price trends in the global PV industry.
Loom Solar unveils 730 W modules, 1.2 GW factory plan in India
India’s Loom Solar says it will build a 1.2 GW module factory in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh and expand production of high-efficiency tunnel oxide passivated contact (TOPCon) and heterojunction (HJT) modules.
How to reduce PV module temperature with frame perforations
Scientists in China have investigated how frame perforations can help reduce the operational temperatures of solar modules through air cooling. Their findings show that the number of perforations must be carefully calibrated, and that more is not necessarily better.
Mexico leads Latin American countries in global silver production
Commodity Trading Club (CTC) says Mexico, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina together supply more than half the world’s silver output, a cornerstone metal for solar and clean-tech industries.
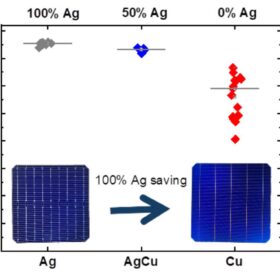
Forschungszentrum Jülich achieves world record 23.08% efficiency for copper-metallized heterojunction solar cell
The cell reportedly exhibits only a 0.4% efficiency loss compared to a reference device that underwent full silver metallization.
Researchers develop antimony-doped n-type silicon ingots to enhance solar module mechanical strength
An international team is proposing to use antimony-doped Czochralski-grown silicon as an alternative to n-type silicon for photovoltaic applications. Their analysis showed that 140 μm as-cut planar antimony-doped wafers exhibit slightly higher mechanical strength compared to common wafers doped with phosphorous.
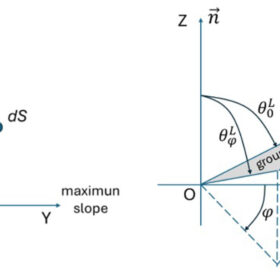
New simulation tool to measure angular losses in PV systems
Researchers in Spain reviewed six models used to calculate incidence angle modifier (IAM) losses in photovoltaic systems. They identified the Martín-Ruiz model as the most comprehensive, as it uniquely accounts for additional angular losses caused by soiling.