Sliding shutters integrate PV for building facades
German manufacturer Ehret has launched SolarSlide, a sliding shutter with integrated PV modules developed with the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (Fraunhofer ISE). It provides solar shading while generating electricity for residential and commercial facades.
InfinityPV releases new compact solar simulator
The Danish company says its new product is ideal for small to medium-sized solar cell testing. It can simulate light conditions in the 390–700 nm range.
Africa’s next growth frontier: Why agrivoltaics are worth the long-term bet
Africa has abundant sunlight, arable land, and innovative farmers, and agrivoltaics offers a long-term strategy to boost food security, climate resilience, and energy access simultaneously. Success depends on coordinated policy, inclusive community engagement, and patient, innovative finance to build a viable, scalable market.
Lightweight PV modules could unlock more than 85 GW of untapped rooftop potential in Europe
In its second monthly column for pv magazine, the Becquerel Institute explains that Europe has vast commercial and industrial rooftops suitable for solar, but decades-old structural limits block conventional PV panels, creating an 85 GW untapped potential. Lightweight PV modules, commercially available and up to 50% lighter, can unlock this constrained market, meeting regulatory, economic, and technical needs for solar deployment across the continent.
Survey highlights technology shift in utility-scale solar
Bifacial PV modules, string inverters and advanced trackers are becoming the preferred technologies in utility-scale solar project design, according to new data from RatedPower.
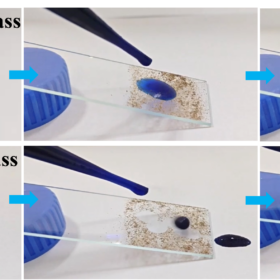
Transparent superhydrophobic self-cleaning coating increases solar cell efficiency by 4.75%
Researchers have developed a PFAS-free dual-layer sol-gel and hydrophobic silica coating that repels water, dust, and dirt while maintaining high light transmission for solar panels. The transparent, self-cleaning coating improved photovoltaic efficiency from 13.90% to 14.56%, demonstrating strong durability and potential for future commercial applications.
Longi launches fire-resistant solar module for rooftop PV
The Chinese manufacturer has launched a fire-resistant version of its Hi-MO X10 module for distributed PV applications, featuring back-contact technology and up to 24.8% efficiency. The company says the module adds enhanced fire-safety design to address rooftop PV risks such as hot spots and DC arcing.
TOPCon solar modules show self-healing under UV stress
Researchers from Nanchang University and Trina Solar found that TOPCon solar modules exhibit metastable “degradation–recovery” under UV exposure, with light soaking fully restoring performance and no impact on real-world energy yield. Their findings highlight the need to refine UV testing standards to better reflect field performance and guide PV reliability assessments.
First attempt to build solar modules using polycarbonate encapsulant
Canadian researchers proposed a laminate-free solar module using polycarbonate instead of EVA and glass. The new encapsulation technique reportedly enables easy disassembly, reuse of solar cells, and open-source local manufacturing.
Water-spray cooling can improve PV module efficiency by 28% in arid environments
An Algerian research team has developed a smart water-spray cooling system for PV panels that activates only when temperatures exceed a set threshold, boosting efficiency while minimizing water use in desert conditions. The system raised power output and reduced module temperatures, offering similar efficiency to continuous cooling but with far lower water consumption, pump operation, and costs.