OCI secures $1.2 billion polysilicon order from Hanwha Solutions
OCI will supply polysilicon from its manufacturing facility in Malaysia, which is expected to have an annual capacity of 35,000 metric tons by the end of June.
Pin-probe bar for busbar-free solar cell production
Japan’s Kopel has developed a device with a thickness of just 1.2 mm, with contacts on all of the finger electrodes of busbar-less solar cells.
Solar panel glut causing messy ‘false economy’ in Australia
Global solar supply chain issues and the Chinese energy crisis, which hit in the second half of last year, have ironically led to a “massive” oversupply of solar panels in Australia, according to major distributors. The tension between higher global panel costs and the glut of them within Australia has led to some messy pricing and strange market dynamics on the ground.
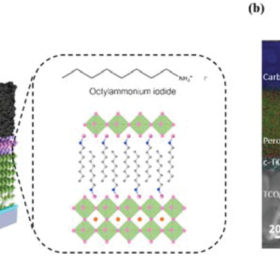
Electron blocking for 18.5%-efficient carbon-electrode perovskite solar cell
Scientists in Germany and Switzerland have developed a perovskite solar cell with a carbon electrode that achieved 18.5% efficiency. It also retained 82% of this after 500 hours of continuous illumination. While a long way behind what has been achieved with other perovskite solar devices, the cell is produced via all low-temperature processes that could likely be scaled into low-cost, large-scale manufacturing – making the approach one worth pursuing further.
CubicPV, Waaree sign 1 GW PV cell supply deal
US-based CubicPV will supply 1 GW of Direct Wafer silicon solar cells per year to Indian manufacturer Waaree Energies under a five-year contract. The cells will be supplied from its upcoming 2 GW factory in India.
France defines standards for agrivoltaics
France’s environmental agency Ademe has released a set of new guidelines that clearly define “agrivoltaics.”
Photovoltaics vs. nuclear power on Mars
Solar might be more efficient than nuclear energy to supply power for a six-person extended mission to Mars that will involve a 480-day stay on the planet’s surface before returning to Earth, according to new US research.
SEIA cuts PV forecast 46% due to anti-circumvention investigation
The latest update to the Solar Energy Industries Association’s (SEIA) survey for solar workers and companies shows drastic outcomes for the industry if tariffs are imposed on countries under investigation.
MIT, NREL researchers develop 40%-efficient thermophotovoltaic cell for grid-scale thermal batteries
The device is described as a heat engine with no moving parts that is able to produce power from a heat source of between 1,900 to 2,400 C. This concept is known as thermal energy grid storage (TEGS) and consists of a low-cost, grid-scale storage technology that uses thermophotovoltaic cells to convert heat to electricity above 2,000 C.
Trimaran-shaped floating PV system design from Spain
The proposed system architecture is claimed to offer more stability compared to conventional floating structures and reduces by up to 93% the contact area of the system with the water. The first system prototype was recently developed on a water reservoir in Alava, in the northeastern territory of the Basque Country.