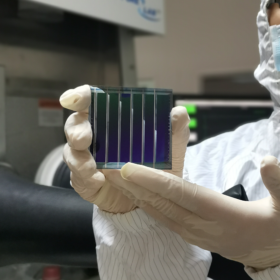
South Korea bets on tandem solar technologies
The South Korean government has released a new roadmap to support R&D activities in the solar sector. The document indicates the country’s solar manufacturing industry may be encouraged to opt for high-efficiency and expensive panels based on tandem solar cells.
Senegal introduces VAT exemption for off-grid solar products
The Senegalese government is aiming to increase access to solar power in rural areas by reducing VAT on PV panels, inverters, solar thermal collectors and other products in an effort to achieve universal electricity access in the country by 2025.
Light and shade of 500 W plus solar panels – part III
In the third article in a series, pv magazine editor Pilar Sánchez Molina and industry experts continue their discussion on the challenges and opportunities created by new panels with power output exceeding 500 W.
Organic solar module with 14.4% efficiency
Scientists in China have developed an organic module with an area of 18 cm2 based on a non-fullerene acceptor called DTY6. The device has a certified efficiency of 13.98%, but when a non-halogen solvent was used, it even reached 16.1%.
Chinese PV Industry Brief: New EVA encapsulant factory, 1 GW PV pipeline
Cybrid, a Shanghai-listed backsheet supplier, will open a new EVA encapsulant factory in Zhejiang province. Datang, meanwhile, has revealed plans to build 1.05 GW at 10 sites across three provinces.
Light and shade of 500 W plus solar panels – part II
In the second article in a series, pv magazine editor Pilar Sánchez Molina and industry experts keep discussing the challenges and opportunities created by new panels with power output exceeding 500 W.
Scaling up solar manufacturing in India
A new study by the CEEW Centre for Energy Finance assesses China’s advantages over India, but presents ways for the South Asian nation to build a competitive PV manufacturing sector.
Enphase microinverters for high-power modules
The US microinverter manufacturer has now brought its inverter solution for commercial and industrial solar to Australia and Europe. The device is suitable for modules with power output ranging from 295 to 450 W and has a European efficiency of 96.5%.
Light and shade of 500 W plus solar panels – part I
In the first article of a series, pv magazine editor Pilar Sánchez Molina analyzes with industry experts challenges and opportunities created by new panels with power output exceeding 500 W.
New dopants may improve PV glass performance
According to a British-Swedish research team, the down‐shifting process for solar glass manufacturing can be improved through the use of two dopant cations that produce no absorption bands. The doping with these compounds is said to reduce the UV transmission while also keeping the glass free from absorption in the visible and near-infrared ranges.