Post SNEC: Market demand and technology trends
Every year, the SNEC PV Power Expo marks a turning point in the direction of solar market trends, and 2021 was no exception. Corrine Lin, chief analyst at PV InfoLink, was at the show to soak up the latest trends at one of the first big events to go ahead since early 2020.
Europe’s gigafactory boom – 25 by ‘25
A gigafactory, as the name indicates, is a facility that aims to produce Li-ion cells at a gigawatt-hours scale of total capacity, so they can then be used in electric vehicles or stationary storage applications. The global production capacity of Li-ion cells is expected to reach 740 GWh by the end of 2021 – almost a threefold increase from 2017 – and Europe will account for 8% of the total. João Coelho, an analyst at Delta-EE, looks at how Europe plans to catch up.
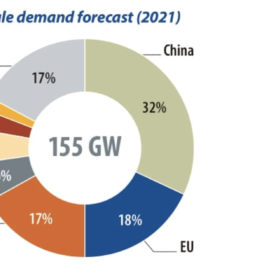
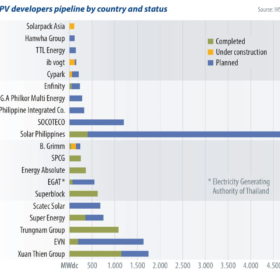
Southeast Asia’s big PV plans – 27 GW by 2025
PV markets in Southeast Asia have picked up over the past two years, driven by the astounding growth of Vietnam. Regional policies, combined with growing demand for renewable power in the manufacturing industry, will result in 27 GW of new PV installations across the region over the next five years, writes IHS Markit analyst Dharmendra Kumar. PV installations in these countries are driven by attractive feed-in tariffs, net energy metering, tariff-based auction mechanisms, and other incentives.
Strong growth predicted for Middle Eastern solar PV
The Middle East, and the Gulf in particular, has been home to record low solar tariffs in recent years. Major projects are being awarded via tenders, with prices gradually closing in on a remarkable 1 USDct/kWh. Of course, this is no coincidence due to the region’s favorable solar conditions: availability of cheap and sunny desert land, low labor costs, cheap project financing, supportive tax regimes, large projects benefitting from economies of scale, well designed tender structures, and decreasing PV component prices.
Politicians tend to overpromise, except when it comes to solar
The speed of all transitions is inherently underestimated, and solar PV is no exception. The EU has grossly underestimated its coming of age, as its forecasts for 2020 were off by 67% for the Netherlands and 74% for Germany, writes Rolf Heynen, CEO of Dutch New Energy Research.
Carbon neutrality and solar’s role in ASEAN nations
The Paris Agreement has been signed by all ASEAN nations and almost all members have declared a carbon emissions reduction target. The diversity in ASEAN’s readiness for energy transition is reflected in the wide-ranging nationally determined contribution targets set for reducing greenhouse gases. An immediate quick win for the renewable energy transition is the harnessing of solar power from an abundance of resources in the region.
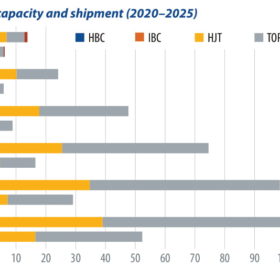
N-type solar development
This year, PV cell manufacturers will face the challenge of transformation. Apart from adjusting the ratio of production for different-sized cells, some manufacturers are turning to next-generation opportunities, shifting investment from p-PERC to n-type technology. PV InfoLink Analyst Amy Fang discusses the issues facing n-type cell development this year.
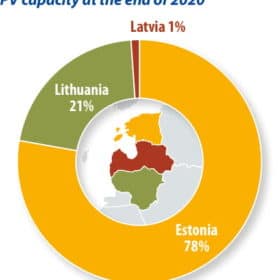
PV policy developments in the Baltic states
Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania have seen uneven development in PV installations to date, and the three Baltic states are still highly dependent on imports from Russia. Estonia needs to replace aging energy infrastructure, and so far it has led the region in PV deployments. Latvia, meanwhile, has a high level of hydro in its energy mix, and less incentive to build PV. IHS Markit analyst Susanne von Aichberger examines the latest policy developments in the Baltic states.
IHSM clean energy insights: High module prices and shipping costs jeopardize 2021 installation outlook
In the first installment of a new monthly blog by IHS Markit, Edurne Zoco, executive director for clean energy technology, writes that high prices and increased freight costs are putting solar PV procurement teams under extreme pressure, particularly those teams with connection deadlines this year that were anticipating a more favorable pricing and logistic environment in the second half of 2021.
Turning Nepal’s solar game around
Until 2016, Nepal suffered from chronic power shortages. At that time, just 65% of the country’s population had access to electricity. Assessing the situation, the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) estimated that the country has the potential for 2.1 GW of installed PV capacity. Although the Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA) has officially been able to buy solar power under long-term PPAs since July 2014, the majority of projects granted these contracts have been large-scale hydropower plants. Following slow activity, plans are finally afoot, however, to boost the country’s solar footprint.