Kenya to combat rural energy access gap with over 130 solar minigrids
Kenya’s government plans to build 137 solar minigrids across remote locations in the East African country. The project received $150 million in funding from the World Bank.
Solar, storage system for water treatment in Malawi
RIC Energy has built a 1.3 MW PV array and a 4.5 MWh battery system for two water treatment plants and five water pumping stations in Malawi. The hybrid system will treat enough water to supply more than 200,000 people.
Sterlite Power commissions 5 GW green energy corridor project in India
Sterlite Power’s Lakadia-Vadodara transmission project will deliver more than 5 GW of electricity from the Indian state of Gujarat to the rest of the country.
Forecasting model to manage renewables-powered grids
Scientists in South Korea have developed a forecasting model to better manage electric grids with high penetration of intermittent renewables. The model was tested using historic data from Pennsylvania-New Jersey-Maryland (PJM) grid in the United States, and shown to accurately forecast the availability of renewable energy resources up to one day in advance.
Pumped hydro key to meeting storage demand
Pumped hydro energy storage can be readily scaled to any required storage capacity at a known and affordable cost.
Inverter sizing guides grid connection, rules US court
The US Court of Appeals has ruled that an 80 MW (AC)/160 MW (DC) solar farm, with 50 MW of battery storage, meets “Qualifying Facility” status of 80 MW (AC) or less under the Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act (PURPA) of 1978.
German machinery unlocks onsite transmission line recycling in Australia
Australian grid operator Transgrid has partnered with German machinery manufacturer Zeck for the use of its innovative steel separation tech. Zeck’s machine can process electricity transmission lines into a recycle-ready state onsite. Previously, Transgrid sent old transmission lines offshore for this process at a much higher cost.
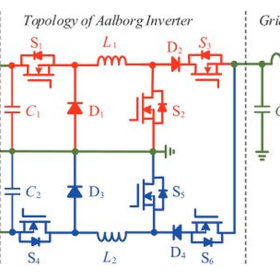
New Aalborg inverter design for PV applications
An international research group has developed a new Aalborg inverter design for high-power applications in solar arrays. The device has fewer switches than conventional, voltage-source inverters and can reportedly improve PV system performance by reducing switching losses.
UK power capacity auction delivers 627 MW of battery storage
Britain’s T-1 Capacity Auction for delivery in the 2023-24 period saw battery energy storage technology emerge as the third-biggest winner in terms of secured contracts, following gas and nuclear. Batteries accounted for more than a half of the new build capacity.
Curtailment is not the enemy
A new report by IEA-PVPS Task 16 looks at the use of “implicit storage” to transform intermittent renewable sources such as solar and wind into firm power generation. It shows that the total cost of the electricity system transformation could be lowered with the optimal use of capacity overbuilding and dynamic curtailment.