BayWa, Velux sign Europe’s first agrivoltaics-linked PPA
Germany’s BayWa r.e. and Denmark’s Velux have announced the first agrivoltaic corporate power purchase agreement (PPA) in Europe. BayWa will build two solar parks in Spain to power Velux’s operations, with capacities of 60 MWp and 56 MWp. One of them will partly be an agricultural PV project.
US battery maker unveils solid-state storage systems for residential applications
Amptricity has emerged from stealth mode with plans to manufacture solid-state batteries for residential and commercial installations.
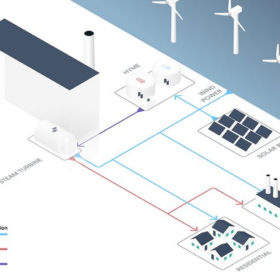
The Hydrogen Stream: GKN Aerospace delivers ground-based liquid hydrogen fuel system demonstrator
GKN Aerospace has demonstrated the feasibility of using a liquid hydrogen fuel source to increase the endurance of uncrewed aerial systems (UAS) for search and rescue. Germany, meanwhile, has announced €550 million ($572 million) of fresh funding for hydrogen projects across the world.
Photovoltaic signboard with 18.5% efficiency
Dansk Solenergi, a Danish building-integrated PV specialist, has launched a round, 95 W solar module that works as a PV signboard. Its 35 solar cells, which remain hidden behind an image of Earth, have an efficiency of 18.5%.
JinkoSolar claims 23.86% efficiency for n-type, TOPCon monocrystalline panel
JinkoSolar’s newest PV module has an efficiency rating of 23.86%. It is based on its TOPCon mono cell tech, which achieved a record efficiency of 26.1% in October, as confirmed by TÜV Rheinland.
Roadmap to increase solar acceptance
The PV sector has significant implications for the economy, society and the environment. Positive impacts show that PV is a key contributor on the path to sustainability, and that highlighting these benefits could raise social and political acceptance in the transition to sustainable energy.
Danish consortium builds 1 MW/20 MWh molten salt thermal storage facility
Hyme Energy and Bornholms Energi & Forsyning are building a pilot project to store clean electricity with molten salt. The system will likely start providing heat, power and ancillary services by 2024.
New algorithm to identify underperforming strings in PV systems
German researchers have created an algorithm to predict and identify string yield losses or underperforming strings without additional weather data. It could be used to inspect modules, strings, arrays, inverters, and transformers.
The mobility rEVolution: Carmakers set to make more ICE cars than sustainable
Global production of internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles is on track to far exceed sustainable levels from a climate perspective, according to a new German-Australian study. Foxconn, meanwhile, has started building an EV factory in Thailand.
Floating ‘artificial leaf’ for solar-to-hydrogen production
University of Cambridge scientists have developed lightweight floating photocatalyst devices that produce green hydrogen and syngas. The leaf-like photoelectrochemical devices show potential for scalability.