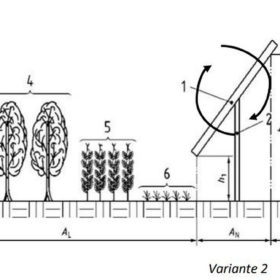
Italian solar sector defines standards for agrivoltaics
A document compiled by three Italian renewables associations identifies with extreme precision the area that is allowed to be used for power generation in the two most common agrivoltaics configurations — solar arrays with elevated solar modules and PV systems deployed between crop rows.
The Solar Tech Check: PV in space, and thin films stride forward
This week has seen NASA announce the completion of a new folding array set to power a mission deep into our solar system, while scientists continue to work on new applications to take such explorations even further from the sun. New measurements also promise routes to higher efficiency in cadmium-telluride PV, and details emerge of one of thinnest solar cells seen so far.
Photovoltaic forced ventilated facade for applications with air source heat pumps
Scientists in Spain have designed a BIPV forced ventilated facade that can be used as support for heating and a domestic hot water (DHW) building system based on air source heat pumps (ASHPs). In the proposed system configuration, the heat pump is expected to cover building heating demand at all times, regardless of the performance of the solar array.
Solar caravan powering the electric vehicle that tows it
The solar modules for the solar array were supplied by Chinese manufacturer Longi, which is a major partner in the project.
Solar-plus-food in ethanol fields could fully power the United States
The conversion of the 40 million acres of ethanol corn farms in the United States into solar-plus-food facilities could generate 1.5 times the nation’s electricity needs, while also powering a 100% electrified passenger vehicle fleet.
Rocket Lab unveils space solar cell with 33.3% efficiency
The new device is based on an inverted metamorphic multi-junction (IMM) cell technology developed by Rocket Lab’s unit Solaero. The cell can be used in applications in the civil, military, and commercial space markets.
Solar desalination via floating PV in Spain
The Agua+S project under development in the Spanish region of Andalucia is aimed at combining a desalination plant, a pumping station network, and an onshore, floating photovoltaic plant in a single project design. According to its developers this is the first time that these three facilities have been combined together in a fully reproducible design that could be replicated in any river basin that has a reservoir and is close to the coast, to produce fresh water for both irrigation and human consumption.
Solar cells based on 2D carbides, nitrides
Researchers from Qatar and South Korea have studied the potential of solar cells based on 2D MXenes materials. They said that titanium carbide MXene (Ti3C2Tx) is the most promising material in the MXene family for PV applications.
Panasonic launches solar heat pump solution for water heating
Panasonic has unveiled a new product in Japan with a PV-based charging function that uses a heat pump and hot water storage unit to save energy by maintaining bathwater temperatures at constant levels.
Fully autonomous robot for solar O&M
OnSight Technology has developed a tele-operated vehicle to clean solar arrays. It is equipped with a radiometric thermal imaging camera and an optical zoom camera backed by artificial intelligence. It has a range of 12 hours and a speed of 1.6 km per hour.