Utility scale solar reaches LCOE of $0.028-$0.041/kWh in the US, Lazard finds
Lazard’s newly released Levelized Cost of Energy Analysis 15.0 and Storage 7.0 reports that solar and wind are the most competitive electricity sources in the US energy market. According to the investment bank’s 2021 study, gas combined cycle has the lowest LCOE of $0.045-$0.074/kWh among the conventional sources and that of coal and nuclear is $0.065-$0.152/kWh and $0.131-$0.204/kWh, respectively.
210mm wafer achieves highest energy yield, finds Trina Solar
Trina Solar has found that its Vertex modules, based on the 210mm wafer, achieve an energy yield up to 1.6% higher than rival products based on the smaller 182mm wafer format. The company conducted outdoor testing at two separate sites with varying climates, finding that products based on the larger format have a particular advantage in low-irradiance environments.
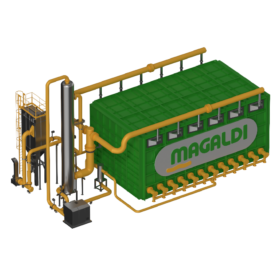
Long-duration thermal storage system based on silica sand
Developed by Italian dry bottom ash handling system provider Magaldi Power, the system produces green thermal energy — steam or hot air — which can be used directly in industrial plants or for the generation of electricity using steam turbines. The system consists of a blower, a fluidization air blowing system, a fluidization air suction system, an air filter and fan, an air pre-heater, and an integrated thermal energy storage module. Silica sands are the system’s storage media.
Redback unveils solar inverters, expands battery range
Australian energy storage specialist Redback Technologies has unveiled a newly expanded product range. It has added a series of grid-tied solar inverters and new beefed-up battery products to its line of modular storage systems for residential and commercial customers.
How the numbers may work for 50-year solar
The discounted cash flow from a solar project’s electricity generation increases by 46% when shifting the installation from today’s standard 25-year lifetime to a 50-year time scale.
Duracell launches 14 kWh battery for residential PV
The US battery manufacturer entered the stationary storage business with a new product for residential customers. The lithium iron phosphate (LFP) battery is compatible with new or existing PV systems.
Remote sensing-based GIS model to identify pumped hydro-suitable locations
Proposed by Egyptian scientists, the proposed GIS technique considers a pumped-hydro project’s head and elevation difference, the penstock-length distance from the base plant, the site’s slopes and slope of the ground surface, the distance to the national grid and road networks, and the soil suitability. It also takes into account constraints such as land use and restrictions.
Lead absorbing encapsulant for perovskite solar cells
Scientists in the United States developed what they describe as a ‘scotch-tape like’ solution, which can absorb potential lead leakage from perovskite solar cells, preventing the toxic material from entering the environment. The tape, according to the scientists, can easily be integrated with existing encapsulation strategies, and was shown to absorb 99.9% of lead leaked from cells from that were severely damaged.
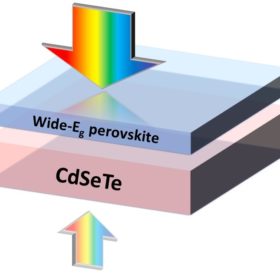
Bifacial tandem perovskite-CdSeTe solar cell with 20% efficiency
Developed by U.S. scientists, the cell is claimed to achieve an equivalent bifacial efficiency of more than 20% with an open-circuit voltage of more than 2 V. The choice of the bifacial architecture is intended at increasing the device’s power yield in order to offset the high costs for producing the CdSeTe sub-cell.
Ideematec unveils one-in-portrait solar tracker
The horizontal single-axis tracker has the typical size of 195×2.5m and its tracking range is 55 degrees. The new product is an evolution of the company’s two-in-portrait solution and was conceived to meet the increasing demand for one-in-portrait trackers.