Imec hits 27.1% on perovskite/silicon tandem cell
Belgian research institute, Imec has announced the achievement of 27.1% efficiency on a perovskite/silicon tandem cell, providing further evidence of the technology’s potential to provide a low cost efficiency boost to existing PV technology.
Video: Future PV Roundtable @ Intersolar Europe 2018
Peijun Shen of Huawei discusses integrating bifacial modules into PV power plant projects from the Future PV discussion at this year’s Intersolar Europe. Bifacial technology is making leaps and bounds, and suppliers up and down the value chain have to deliver new technologies and solutions to pave the way for the next steps in PV systems.
Italy: Glass to Power crowdfunds €2.25 million, plans solar window fab
Italy-based Glass to Power has raised €2.25 million via crowdfunding to advance its plans for the roll out of an industrial production line for its transparent solar PV windows. The product is expected to be marketed in 2019.
The weekend read: CIGS is back, back again
Stability and reliability, partial transparency, monolithic deposition onto flexible substrates, aesthetically pleasing appearance, applicability in roll-to-roll production, superior temperature coefficient, potential in tandem applications, and suitability for BIPV: The list of advantages that CIGS technology offers is well established and lengthy.
Global energy investment in 2017 moved away from energy security and sustainability goals, finds IEA
Following a strong year for clean energy spending, 2017 saw a 7% decline in renewable power investment – to around $298 billion – while the share of fossil fuels in energy supply funding rose for the first time since 2014, according to the International Energy Agency in a report published today.
US researchers achieve breakthrough for graphene-based solar cells
A team of scientists at the University of Kansas has developed a method to boost the lifetime of excited electrons in graphene, a development which the team alleges could lead to the development of highly efficient, ultrathin solar cells.
EPFL Scientists develop 25.2% efficient perovskite/silicon tandem cell
Researchers from the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) in Switzerland have developed a process for depositing a perovskite layer onto a silicon solar cell, which it says has already resulted in the creation of a 25.2% efficient tandem cell.
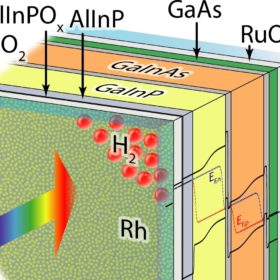
New solar water-splitting cell demonstrates 19.3% efficiency, increasing longevity significantly
The cell uses a novel approach that increases its conversion efficiency and longevity at the same time. Researchers claim it is a new world record for this type of application and highlight its importance in storing renewable energy in hydrogen to compensate for output and demand fluctuations.
Amount of silver needed in solar cells to be more than halved by 2028, Silver Institute says
The US-based industry association finds the amount of silver loading may fall from 130 mg per cell in 2016 to approximately 65 mg by 2028. Alternative and cheaper raw materials, such as copper and aluminum, are not expected to replace silver in commercial cell production, at least in the next decade.
New bacteria-based solar cell doubles density, reduces production cost
Researchers coated bacteria with a semiconductor before application to an anode glass. This process is reportedly cheap and taps energy produced by the bacteria through photosynthesis. Additionally, the researchers state power output is not impeded by overcast skies, making it ideal for northern Europe, Canada, mines and other low-light environments.