Fast charging for lithium-ion batteries needs a fix
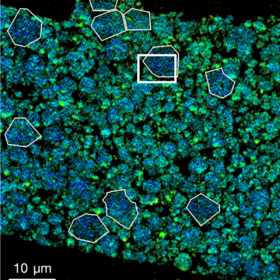
Scientists in the United States placed fast charging for lithium-ion batteries under the microscope, finding that charging at higher rates can quickly damage the structure of a graphite anode, causing capacity loss even after a small number of cycles. By identifying the mechanisms causing this performance loss, the group can help point future research in the right direction.
New ‘bioinspired’ solution to battery degradation
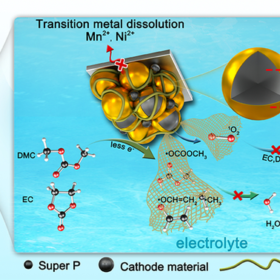
As part of their efforts to bring lithium-ion battery degradation under control, scientists in China have looked to emulate natural defenses many organisms have evolved to reduce oxidation reactions and related damage. With an additive that ‘scavenges’ reactive particles before they can contribute to degradation, the group was able to demonstrate significantly lower electrolyte decomposition in a working battery.
Behind the price drops in lithium-ion batteries
Scientists in the United States pieced together data from hundreds of different sources, looking to establish the key factors that have led to consistently falling prices for lithium-ion technology since their commercialization thirty years ago. They find that public-funded research, primarily in chemistry and materials science, has made the largest contribution to cost reduction. And they offer suggestions on policy and investment to ensure that the research can continue to make these important contributions to reduction in battery costs.
Panasonic launches new Evervolt battery
Panasonic said the system is available in the U.S. with storage capacities of 17.1 kWh and 25.65 kWh. The product comes with a floor-standing battery cabinet and a hybrid smart inverter with 4 MPPTs.
‘World’s largest lead-acid battery output’ planned in Greece
Manufacturer Sunlight plans to invest €30 million to add 1.3 GWh of annual production capacity of lead-acid products by the third quarter of next year. The company will also devote €20 million to expanding its lithium-ion battery assembly lines.
New alkali metal-chlorine battery promises 6x energy density
Scientists in the U.S. discovered a promising new battery chemistry based on chlorine and table salt. Batteries based on this chemistry can achieve at least six times the energy density of today’s lithium-ion batteries, according to the group that created it. The prototype battery could already be suitable for small devices such as hearing aids, and with further work could be scaled up to larger applications.
Energy storage appears to be fully charged for exponential growth
Lithium-based energy storage volumes are expected to grow by multiple orders of magnitude in the coming years, with a 1,000% capacity increase by 2023.
Maxeon secures EU cash to make its ‘stick-on’ solar panels in France
The TotalEnergies-controlled solar manufacturer will secure an, as yet undetermined chunk of a new €118.6 million low-carbon innovation fund to start producing its frameless, glass-free solar roofing products at Porcelette, in northeastern France.
Hold your breath for a better battery
Recent research has revealed a previously underestimated role for oxygen in limiting the performance of lithium-ion batteries. Newly published research from both Japan and the United States has sought to look deeper into the chemical reactions at the heart of lithium-ion storage; and to better characterize the cumulative effects that minuscule amounts of oxygen released during these reactions can have on battery performance and safety.
Another battery recycling plant for Sweden
Construction on the Halmstad facility is expected to start this year after the Stena Recycling branch of the Swedish conglomerate announced a €25 million commitment.