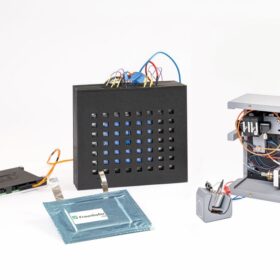
World’s first high-power aluminum-ion battery system for energy storage
For the first time, a complete aluminum-graphite-dual-ion battery system has been built and tested, showing that lithium-free, high-power batteries can deliver stability, fast response, and recyclability for next-generation grid applications.
Keeping the smart grid cyber secure
As smart grid tech is rolled out around the world to modernize legacy assets and integrate renewable energy generation, it is also making the electricity network more prone to cyber attacks. IEC Standards provide protection but they also are challenged to keep up with the latest threats.
Cooling PV modules with seawater
A research team in India developed a passive solar-panel cooling method using a thin, still layer of seawater placed over the module surface. Tests showed that while a thick water layer sharply reduced energy output, a thin 5 mm layer lowered module temperatures and increased daily energy generation by up to 8.86%.
Panasonic testing PV-driven hydrogen platform in Germany
The Japanese conglomerate has deployed its Panasonic HX hydrogen solution at its facility in Munich. The system uses an AI-based energy management system that reportedly makes battery storage unnecessary.
Offshore solar could achieve LCOE of less than $0.06/kWh in Thailand, Malaysia
An international team of researchers completed a preliminary techno-economic study on the global potential for offshore floating PV (OFPV). The results provide project cost benchmarking, country-specific economic assumptions, and a global assessement of offshore solar’s levelized cost of electricity (LCOE).
Chinese researchers build 31.71%-efficient perovskite-silicon tandem solar cell based on new interfacial engineering
The two-terminal perovskite–silicon tandem solar cell was fabricated through a chemical polishing method that selectively removes residual lead(II)iodide from the perorvskite film in the top cell. This targeted interfacial engineering improved uniformity and stability, enabling a certified 31.71% efficiency and enhanced long-term performance.
How to build giant solar plants in mountainous areas
Chinese researchers have proposed a new methodology for designing utility-scale solar power projects in mountainous regions. They simulated a 386.4 MW solar farm near Pu’er, a city in southern China located 1,037 meters above sea level.
Fraunhofer ISE achieves 30.6% efficiency for perovskite-silicon tandem based on industry-standard bottom TOPCon cell
Researchers at Fraunhofer ISE have developed a perovskite-silicon tandem solar cell using a TOPCon bottom cell with standard textured front surfaces. Their results show that TOPCon bottom cells can perform comparably to heterojunction cells in tandem devices in terms of shunt resistivity, supporting scalable, cost-effective industrial production.
Agrivoltaics for sorghum, soybean grain
Researchers in the United States found that shading from agrivoltaic systems reduces grain numbers in both sorghum and soybean, but sorghum can partially compensate by increasing grain weight while soybean cannot. The study shows that sorghum and soybean respond differently due to their physiology, offering guidance for crop selection and management to minimize yield penalties in agrivoltaics.
How to use compressed air storage in flooded coal mines
Researchers in China developed a new compressed air energy storage system that uses flooded roadways in abandoned coal mines to store compressed air and heat for nighttime power generation. Simulations show the design can achieve 71.5% thermal efficiency, stable performance, and higher energy density at greater depths, with minimal long-term impact from air leakage.