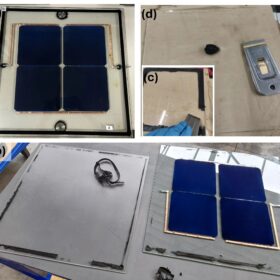
Flexible perovskite solar cells with tunable color, transparency
Researchers at Hebrew University of Jerusalem have demonstrated 9.2% efficient printable semi-transparent, flexible halide perovskite solar cells with tunable color and transparency.
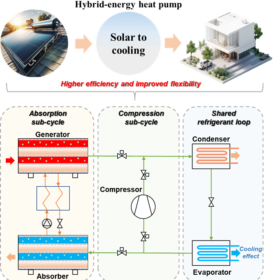
Scientists unveil hybrid-energy heat pump combining absorption and compression cycles
Researchers in Hong Kong have developed a hybrid-energy heat pump that seamlessly combines absorption and compression cycles using crystallization-free ionic liquids, improving efficiency and reliability across varying solar conditions. Simulations in multiple Chinese cities show the system can significantly cut electricity use and cooling costs, making it promising for sustainable building cooling and future commercial scaling.
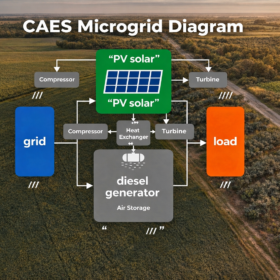
How to combine C&I solar with compressed air energy storage
Researchers have studied the potential of combining photovoltaic systems with compressed air energy storage (CAES) to power a commercial building in South Africa. They found that a co-optimized system could lower total capital costs by 15–20% compared to traditional sequential sizing approaches.
Fraunhofer ISE developing world’s first medium-voltage solar plants
Germany’s Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (Fraunhofer ISE) is developing the world’s first medium-voltage PV plants in Germany to cut material use, reduce costs, and simplify grid integration. They will test 1,500 V and 3 kV string configurations to create cost-effective, voltage-resistant components for large-scale solar.
TU Delft unveils liquid solar module encapsulation tech
TU Delft researchers have developed a liquid-based solar module encapsulation that performs on par with conventional EVA panels while offering improved recyclability and circularity. The approach is compatible with silicon and tandem perovskite/silicon cells and could support thermal management and integration into photovoltaic-thermal modules.
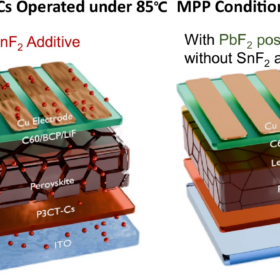
Scientists build tin lead perovskite solar cell with 24.07% efficiency
A Chinese-Swedish research team has boosted the performance of tin-lead perovskite solar cells by modifying additives and post-treatment processes. The device also demonstrated improved stability, retaining 60% of its initial efficiency after 550 hours at 85 °C under maximum power point conditions.
‘Agrivoltaics is not just a land-sharing concept, but a systems-level solution to some of the world’s most pressing challenges’
Scientists have conducted a six-sphere literature analysis of agrivoltaics, considering sustainability, soil–crop productivity, socioeconomic resilience, solar power generation, spatial efficiency, and species. They found that, under optimal terms, agrivoltaics may generate over $1 trillion in added global agricultural income.
French scientists discover new UV-induced degradation pathways in heterojunction solar cells
Scientists from French research institute CEA-Liten have identified hydrogen migration in doped selective layers as the primary driver of UV-induced degradation in silicon heterojunction solar cells. They have also found that combined light and thermal light-soaking treatments can partially restore performance and improve long-term UV stability.
Scientists achieve 32.6% efficiency in perovskite-silicon tandem solar cell via interface engineering
Researchers from KAUST, TU Delft, and LMU Munich have improved the performance of monolithic perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells by modifying the physical structure at the front of the bottom heterojunction solar cell.
More PV manufacturers expected to adopt copper metallization in 2026
Rising silver prices are pushing PV manufacturers toward copper-based metallization, with DK Electronic Materials targeting 2026 for large-scale deployment of high-copper paste solutions, while Fraunhofer ISE warns efficiency trade-offs remain unacceptable.