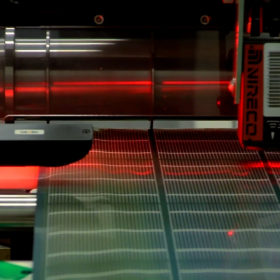
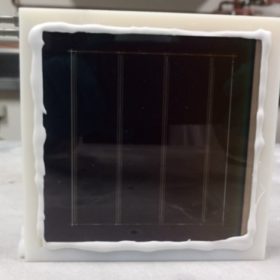
Single crystal perovskite solar cell with 17.8% efficiency
The solar cell was manufactured with crystals that were grown directly onto indium tin oxide (ITO) substrates covered with hole transport layer (HTL). These substrates have a controlled thickness of tens of micrometers and area of tens of mm2. The device showed an efficiency of 17.8%, a short-circuit current of 21.0 mA cm−2, an open-circuit voltage to 1.08 V, and a fill factor to 78.6%.
Cheapest long-duration storage for systems with high renewables
National Renewable Energy Laboratory researchers have studied which tech offers the lowest levelized cost of energy to provide the US Western Interconnection grid with electricity when wind and solar are not available. They assumed 85% renewables penetration and determined that geologic hydrogen storage and natural gas combined-cycle plants with carbon capture storage are the cheapest options for 120-hour discharge applications.
German researchers want to reduce manufacturing costs for electrolysers by more than 25%
A number of Fraunhofer institutes in Germany want to make green hydrogen more cost-competitive and are working to identify the best and most economical processes for the production of electrolyzers. They intend to build a digital library of future-proof electrolyser manufacturing processes with which the investment costs and even the return on investment can be determined in advance depending on the planned production volume.
Spanish consortium wants to simplify hydrogen production through photoelectrocatalysis
Spanish energy giants Repsol and Enagás are planning to build an electrolyzer based on photoelectrocatalysis at an industrial complex owned by the oil company in Puertollano in 2024. The device receives direct solar radiation and with a photoactive material it generates the electrical charges that cause the separation of the water molecule into hydrogen and oxygen.
Fraunhofer CSP develops repair process for PERC solar cells
The performance of the solar cell contacts can be improved with laser-assisted current treatment. The process does not damage the solar cells but only optimizes faulty semiconductor-metal contacts.
Offshore photovoltaics a step closer
Dutch start-up SolarDuck has secured approval-in-principle for its floating offshore platforms. Its 64 kW pilot project on the inshore water of the Netherlands’ widest river was validated by Bureau Veritas.
Heat pump control strategy for solar assisted district heating
Researchers in Spain have proposed two control strategies for the integration of heat pumps in district heating systems assisted by solar thermal collectors. Their technical-economic analysis shows that the proposed combination can reduce reliance on gas while also reducing costs.
Cooling solar panels with thermoelectric modules
The cooling system was made with an aluminum heat sink and a thermoelectric module. The solar panel is cooled exclusively by the thermoelectric device, which is, in turn, cooled down by the heat sink via free convection. According to the scientists that developed the technique, it was able to reduce panel operating temperature by about 10 degrees Celsius.
Australian scientists set out to use wastewater for green hydrogen electrolysis
Australia has the sun, the wind and the space to become one of the world’s green hydrogen export superpowers in coming decades. However, the Sunburnt Country does have a dearth of one ingredient in the green hydrogen equation – freshwater. Thankfully, researchers from Monash University and a group of national water utilities are joining forces to find a way to use wastewater for the process of electrolysis.
Coupling PV-powered electrochemical water splitting with battery storage
A German research team has developed a photovoltaic-electrochemical device for alkaline water electrolysis that can be linked to battery storage. The proposed system configuration can not only smoothen out the PV power fluctuations and facilitate power coupling, but also improve solar to hydrogen efficiency.