Solar exceeds 28 GW in Brazil, including 20 GW of distributed-generation PV
Brazilian developers have already installed at least 2.1 GW of distributed-generation solar and more than 1.3 GW of centralized PV this year. At this average pace of 21.1 MW per day, installers could build 7.71 GW of distributed-generation PV in 2023.
NREL software models lithium-ion battery supply chain
The US National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has unveiled a tool that surveys how changes in costs, battery adoption scenarios, and international actions affect long-term trends in the battery supply chain.
Tesla to build new battery plant in China
Tesla has revealed plans to build a new Megapack battery factory in Shanghai, according to the Xinhua news agency.
Kosol Energie buys 850 MW PV module production line from SC Solar
India’s Kosol Energie is expanding its annual PV module production capacity to 1.1 GW with the installation of a new 850 MW line from SC Solar. It is aiming for 1.9 GW of cumulative PV module capacity by the end of the current fiscal year.
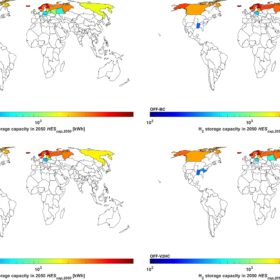
Seasonal hydrogen storage for residential self-consumption
Finnish and German researchers have assessed the role of seasonal hydrogen storage for PV prosumer households with a “least-cost” model at a global level up to 2050. They have found that seasonal hydrogen storage can only be expected in a niche, off-grid market.
Rock-based thermal energy storage production moves into gigawatt scale
Israeli company Brenmiller is set to launch a 4 GW to 5 GW production line for its thermal energy storage systems, which use crushed rocks to retain heat that can be released as steam, hot water, or hot air.
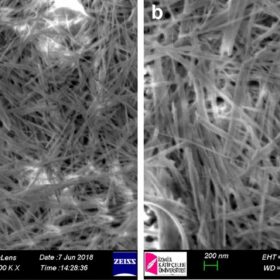
‘Natural clay’ additive promises gains in perovskite solar cell efficiency, stability
Scientists in Turkey have demonstrated that sepiolite, a naturally occurring clay substance, can be added to perovskite precursor materials, and form a scaffold layer that can improve the efficiency and stability of the cells. The scientists believe that this substance could be valuable in developing reproducible processes for the production of large-area perovskite solar cells.
High-efficiency electrodes with ultralight current collectors
Eight industrial and scientific entities in Germany have come together to pursue two key innovations in lithium-ion battery technology: the replacement of metal foils with a metallized fabric structure, and the use of silicon as anode material.
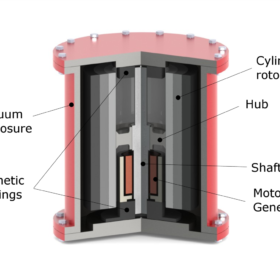
Battery hydrogen vs. battery flywheel
Scientists in Italy have looked at how flywheel storage and reversible solid oxide cells could be integrated with lithium-ion batteries in minigrids powered by solar. They found that flywheels combined with batteries could be the cheapest option for power smoothing.
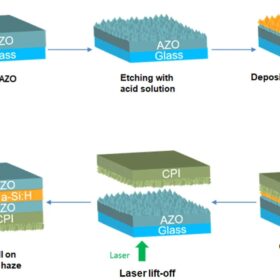
Hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cell for BIPV, bifacial applications
Scientists in South Korea have developed a flexible, transparent solar cell with an average visible transmittance (AVT) of 88.3%. They have also created an n-type rear window layer to optimize bifacial operation.