India tenders 2.45 GW solar power projects with battery storage
Rajasthan Solar Park Development Co. Ltd. (RSDCL) has issued a tender inviting bids to develop 2,450 MW of state transmission utility (STU)-connected solar PV capacity paired with 1,600 MW/6,400 MWh of battery energy storage systems at the Pugal Solar Park in Rajasthan’s Bikaner district. The projects will be implemented on a build-own-operate (BOO) basis.
Solar modules under pressure: The growing risk of spontaneous glass breakage
Once considered isolated incidents, spontaneous glass breakages in solar modules are becoming more frequent, highlighting the limits of some manufacturing choices and the need for closer quality control.
PPA signed for Saskatchewan’s largest solar project
A 157 MW solar project, set to be the largest in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan, will be built following the signing of a power purchase agreement between French developer Neoen and the provincial utility. The project will be co-owned by four Treaty 4 Nations.
The eyes and ears of the power grid
Sensors are an indispensable tool to inform utility managers of the state of the electricity grid and the occurrence of disruptions of any kind. The IEC provides the standards and conformity assessment that enable them to operate safely and efficiently.
MENA region installs 12.2 GW of solar in 2025
Latest report from energy think tank Dii Desert Energy says that with the Middle East and North Africa’s project pipeline of renewables now standing at 202 GW, solar is likely to drive the region past its aggregated national ambitions for renewables of 235 GW by 2030.
Nextpower, Abunayyan to build 12 GW solar tracker factory in Saudi Arabia
The factory will be located in Jeddah and supply solar trackers across Saudi Arabia and the MENA region.
Canal-top PV for Afghanistan’s massive irrigation project
A team of scientists has simulated covering 20% of the Qush-Tepa irrigation canal with PV panels. To this end, the researchers developed a framework, termed an integrated techno-economic-environmental assessment, that can be applied elsewhere. “It explicitly quantifies energy production, water-evaporation reduction, land-use savings, and economic performance within a single analytical structure,” one of the researchers said.
Hybridization: The new paradigm for a more resilient and competitive renewable market
One of the main benefits of hybridization is the ability to offer more attractive and stable energy products to clients. A hybrid PPA better covers consumption needs, reduces risks associated with the variability of a single source, and allows for more competitive long-term pricing, writes Rodrigo López, head of revenues at BNZ.
Romania installs 2.2 GW of solar in 2025
Romania enjoyed another record year for solar deployment in 2025, taking cumulative capacity past the 7 GW threshold. Utility-scale installations almost doubled year-on-year, buoyed by a favourable regulatory framework.
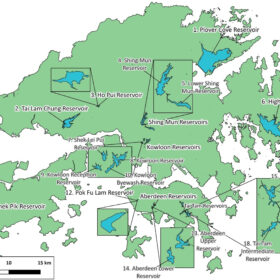
Floating PV could power up to 490,000 households in Hong Kong
Hong Kong has limited land, and researchers have checked how much of the city can be powered if most of its water reservoirs were to be fully or partially covered with floating PV systems. At best, full coverage can supply more than 15% of the city’s total demand, and more than 60% of the residential demand.