Research shows heat pumps perform better than fossil fuel heating in mild cold climates
A British research group has aggregated information from seven field studies on heat pumps from around the world and has found air-source devices have an average coefficient of performance (COP) of 2.74 when temperatures are above −10 C. Below that, COP is between 1.5 and 2.
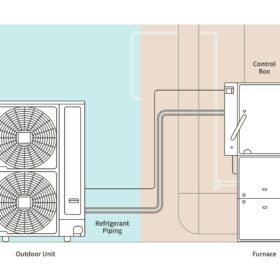
Johnson Controls-Hitachi Air Conditioning unveils residential dual fuel heat pump system
Johnson Controls-Hitachi Air Conditioning has developed a residential dual fuel heat pump system that combines an air source heat pump and a gas furnace. The manufacturer says the furnace is designed to ensure there is no compromise in heating performance, even when temperatures are extremely low.
Printable mesoscopic carbon perovskite solar cell achieves 17.13% efficiency
Scientists in China have built a tandem bifacial mesoscopic perovskite solar cell via a new passivation strategy. The cell achieved an improved power output and voltage, and the researchers said it offers potential applications in practical usage.
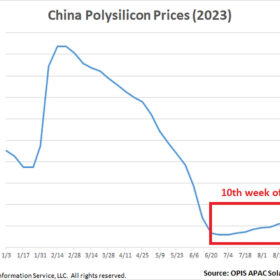
China polysilicon prices extend gains for tenth successive week
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, OPIS, a Dow Jones company, provides a quick look at the main price trends in the global PV industry.
Hybridizing wind with PV may raise value of wind assets by up to 5%
Research from Portugal has looked into adding utility scale PV capacity to wind plants across the country and found the hybridization can significantly increase their market value. The scientists also identified the most critical parameters for forecasting energy generation in hybrid wind-solar plants.
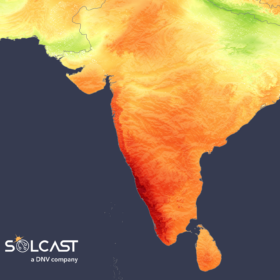
August impacts on Asia’s solar production
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, Solcast, a DNV company, reports that Southern India was the standout in terms of unusual irradiance in Asia in August, with 40% more than the month’s average. This brought the average irradiance up to 6 kWh per day.
Sage demonstrates long-duration storage with underground reservoirs
US-based Sage Geosystems has presented field results showing that its Earthstore underground storage system can provide 18 hours or more of storage capacity, in addition to short-duration power. The solution is said to be cost-competitive with lithium-ion batteries and natural gas peaker plants.
Dubai’s 250 MW/1,500 MWh pumped-storage project nearing completion
Dubai Electricity and Water Authority’s (DEWA) Hatta pumped-storage hydroelectric power plant is now 74% complete, and it is expected to begin operations in the first half of 2025. The facility will also store electricity from the 5 GW Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park.
Single-reagent tech to reuse silicon from end-of-life PV panels achieves recovery rate of 98.9%
Scientists in Singapore developed a single-reagent approach to recover silicon in recycled PV panels that reportedly offers high recovery rates compared to double-reagent methods. The recycled silicon was then effectively reused in anodes intended for applications in lithium-ion batteries.
Three steps to reduce battery storage fire risk
Lithium-ion batteries are generally safe and unlikely to fail, but they can catch fire if damaged, stored, or operated incorrectly. With calls mounting for development of engineering good practice, US-based Firetrace International suggests three steps that battery manufacturers, developers and operators should take into account.