Solar and wind make coal unprofitable in Japan
Recent investments into 11 GW of new coal generation capacity may result in reduced operating cashflows of $71 billion. That will occur, according to a report from the Carbon Tracker Institute, because solar and wind will become cheaper than coal in Japan by 2025 at the latest, despite high renewable energy costs at present.
New configuration gives perovskite cells 18% efficiency
Cesium lead black perovskites could be interesting for solar cell development if their crystals are observed in their less efficient but more stable beta phase. The efficiency shortfall can be solved by healing emerging cracks in the surface of the cell using a choline iodide solution, according to an international team of scientists.
The slow, inexorable rise of green hydrogen
The International Renewable Energy Association says the integration of hydrogen into the energy transition will not happen overnight and electrolysis costs will not be halved until the 2040s. That hydrogen and related products could revolutionize the world energy landscape, however, is not in doubt.
Logic supports renewables, not nuclear
The latest edition of the World Nuclear Industry Status Report gives the energy source little hope in the race against fast, widespread, job-friendly, popular renewables. The report reiterates clean power is taking the lead in the world’s energy system and nuclear is not only too costly a remedy for carbon emissions but too slow to deploy. Nuclear output grew only 2.4% last year while solar and wind power volumes grew 18% and 29%, respectively.
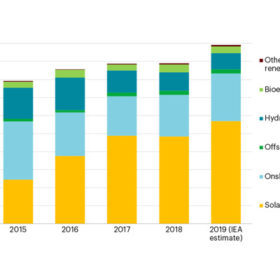
International Energy Agency forecasts 115 GW of new solar this year
The global expansion of PV, wind power and other clean energies will see double-digit growth this year as solar continues to lead the pack.
New Japanese environment minister touts end of nuclear power
After Fukushima, Japan’s nuclear power fleet went offline with plans to restart only when safety concerns could be addressed. On his first day at the office, the new environment minister has said he has no intention of ever restarting the reactors. The move could put Shinjiro Koizumi at loggerheads with PM Shinzo Abe, a vocal proponent of nuclear.
Japan’s largest floating PV plant catches fire after Typhoon Faxai impact
Kyocera’s 13.7 MW floating project at the Yamakura Dam was damaged by 120mph winds the typhoon brought to the coastal city of Chiba. Firefighters said the blaze may have been generated by the strong heat produced by panels stacking up.
Softbank injects another $10m into Swedish dye-sensitized solar specialist Exeger
The Japanese multinational lender is making its second investment in the Swedish start-up. The funds will help the company ship its first products next year.
Japan’s fourth solar auction concludes with lowest bid of $0.098/kWh
The tender produced lower bids than previous rounds but again allocated less generation capacity than planned. The Japanese government initially accepted bids for a combined 589.9 MW but ended up assigning only 195.8 MW of capacity. The final average price for procured solar power was $0.1222/kWh.
Kenyan government blamed for sluggish progress of solar
Two solar farms with 80 MW of generation capacity tendered in 2017 are being built and will be commissioned this year but another two, allocated at the same time, are no nearer construction. Kenya, however, has been touted as the site of Africa’s first wind-solar-storage hybrid project.