Tokyo Gas buys 50% stake in Engie’s Mexican renewable energy unit
The Japanese gas provider has acquired a 50% interest in four Mexican PV projects with a combined capacity of 746 MW. The new joint venture will further develop solar and renewables across the country.
Solar Frontier becomes a unit of Idemitsu
The Japanese CIS solar module maker has been acquired — along with its parent company, Showa Shell Sekiyu — through a share exchange by Japanese oil refiner Idemitsu. The transaction was announced in mid-October, while the preliminary agreement was signed in July.
Japan’s METI cuts C&I FIT by 22%
It is official: METI has cut the feed-in tariff for Japan’s C&I solar segment by 22% to roughly $0.13/kWh.
Japan could install 150 GW by 2030 — report
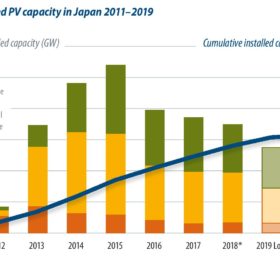
Japan’s cumulative installed PV capacity could reach 150 GW by 2030, from roughly 55.5 GW by the end of 2018, according to a new report by Tokyo based research firm RTS Corp.
A year for transition: Japan’s move beyond the big scale
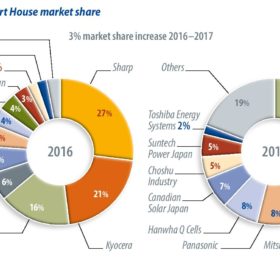
For the past few years, Japan’s solar industry insiders have been eyeing 2019 as a year of transition in the residential rooftop market, as the original 10 year feed-in tariffs come to an end. So, what will this post-FIT landscape look like, and how are Japan’s leading PV suppliers preparing for the future? Hanwha Q Cells’ Japan Marketing Manager Junichi Katayama breaks down the main points.
The weekend read: Zero energy, maximum support
As Japan’s solar appetite shrinks amid questions over everything from falling FIT rates, through the availability of suitable land, to the revival of nuclear generation, Japan’s Zero Energy Homes policies – which require new buildings to integrate with PV and energy efficiency measures – could provide a significant boost to installations. pv magazine looks into Japan’s potential residential recovery.
GCL-Poly backing grid AI application with new joint venture
The Chinese polysilicon heavyweight has joined forces with Japanese industrial and energy conglomerate Mitsui & Co and software company eVolution Networks, and promises to deliver a solution that will beef up the grid.
Nothing boring about Japan’s year of the boar
With tenders coming in for large-scale projects, and decade-old generous FIT programs being phased out, new opportunities and challenges are facing Japan’s PV players. Izumi Kaizuka from Tokyo-based analyst RTS Corporation sets out the major market trends for 2019.
Softbank to invest $10 million in device-integrated solar specialist Exeger
SB Energy Corp, a subsidiary of Japanese multinational Softbank, has announced a strategic partnership with Swedish company Exeger, which produces dye sensitized solar cells designed for integration into consumer electronic devices. Under the terms of the agreement, Softbank Group will invest $10 million in Exeger, with SB Energy Corp set to assist global rollout of the technology.
Smart Energy Week in Tokyo: Self-consumption, storage and a plentiful pipeline for now
Though we’re unlikely to see a return to the days of double-figure GW annual installation levels, Japan will stay at the top table of solar. Last week, pv magazine visited PV Expo Japan, part of Tokyo’s World Smart Energy Week, and found plenty of market developments to discuss, along with healthy interest from major players.