A gulf between PV ambition and testing facilities
Though it already hosts several of the world’s largest PV installations, the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region’s solar industry is still young, with limited local infrastructure and expertise. Project developers are learning quickly that building PV in harsh desert environments requires a careful eye on quality. New testing laboratories are looking to meet demand.
Candi Solar Secures $38 million to support clean energy in Africa, Asia
Philippe Flamand, the director and co-founder of Candi Solar, tells pv magazine about the company’s recent $38 million funding round and its plans to deploy renewables in emerging markets.
The Hydrogen Stream: 20 companies ask Europe to protect electrolyzer industry
Twenty companies have signed a letter to the European Commission, calling for a shift in European industry policy and protections for the electrolyzer industry, while Germany and Morocco have signed a declaration to establish a joint climate and energy alliance.
Tunisian solar module maker Ifrisol targeting US market
Ifrisol, a Tunisian PV module maker, is targeting the US market by producing solar panels with cells sourced from unspecified “non-Chinese” Asian manufacturers.
pv magazine covers Africa Energy Forum in Barcelona
The EnergyNet event brings together more than 2,000 energy decision-makers from Africa at the Fira de Montjuïc in Barcelona from June 25 to 28. The attendees include African governments, utilities, regulators, financial institutions, banks, energy developers, technology providers, and engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) contractors.
Optimized antimony trisulfide solar cells may reach 11.68% efficiency
An international research group has analyzed the most important barriers preventing antimony trisulfide solar cells from reaching satifsfying power conversion efficiencies and has suggested a series of optimization parameters that could get them closer to commercial production.
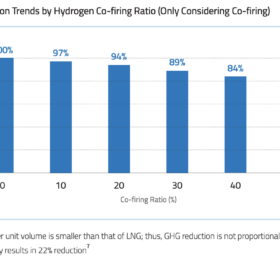
The Hydrogen Stream: Climate group dampens hopes for blue hydrogen
Solutions for Our Climate (SFOC) says in a new report that blue hydrogen might not be an effective climate solution, while TotalEnergies and its partners have agreed to explore green hydrogen potential in Tunisia.
European developer reaches financial close on 10 MW of solar in Tunisia
European renewables developer Qair will build a 10 MW solar plant in western Tunisia with a €3.9 million ($4.2 million) loan from the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD), as well as to up to €1 million in concessional funding from Finland.
Key takeaways from the German-African Energy Forum
The 17th edition of the German-African Energy Forum in Hamburg this week drew more than 300 participants from over 30 countries. The continent’s green energy transition and how to finance it were among the topics on the agenda.
Off-grid solar-wind power plant design for green hydrogen generation
Scientists in Czechia have conducted a techno-economic analysis of a green hydrogen production system powered exclusively by photovoltaic and wind energy. The system uses surplus energy for water treatment and, according to its creator, can achieve a levelized cost of hydrogen of $3.12/kg.