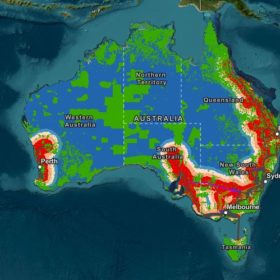
Australian researchers release heat maps for wind, solar project siting
Researchers from the Australian National University (ANU) have unveiled a new online tool to identify the best possible locations for the development of new large-scale wind and solar farms.
US government allocates $8 million to support agrivoltaics
The US government’s FARMS projects will examine multiple configurations of solar system design, crops, and cultivation methods in order to develop replicable models that may offer new economic opportunities.
Agrivoltaics for soybeans
Italian researchers have looked at how soybeans could be grown in agrivoltaic installations and have found that the impact of shading is less significant than previously believed.
Meyer Burger to commercialize 29.6%-efficient perovskite tandem solar cells
Meyer Burger is working with several research institutes in Switzerland and Germany to integrate perovskite tandem technology into its manufacturing processes.
Hydrophobic nanocoating to reduce soiling in solar panels
Scientists in Egypt have created a self-cleaning, hydrophobic coating for solar panels that reportedly increases their efficiency by more than 30%. They used a coating solution based on polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and silicon dioxide (SiO2) nanocomposites, mixed with ethanol and isopropanol.
US organizations publish manual on energy storage safety
The International Code Council and the Interstate Renewable Energy Council (IREC) have published a new handbook on installation codes, hardware standards, and lithium-ion risk-mitigation tools.
Solar Inventions gets patent for silver-saving configurable current solar cells
Solar Inventions has patented technology that could save between $2 million and $5 million per gigawatt in solar projects, while also raising rated power output. The company has patents in the United States, China and Israel for its cell configuration.
Heterojunction germanium solar cell with 8.6% efficiency
Japanese scientists have developed a heterojunction germanium solar cell with the biggest area ever achieved for the tech. It has an open-circuit voltage of 291 mV, a short-circuit current of 45.0 mA/cm2, and a fill factor of 0.656.
Australian researchers use sound waves to expand green hydrogen
Researchers from RMIT University and the University of Melbourne claim that high-frequency vibrations can release 14 times more hydrogen than standard electrolysis techniques. The discovery has ramifications for the expensive, rare materials currently used in electrolyzers.
Aqueous organic flow battery for renewables storage
The Chinese Academy of Sciences has fabricated a kilowatt-scale aqueous redox flow battery with a capacity of 80 mA cm-2 over 500 cycles. The researchers claim that it is a promising candidate for large-scale energy storage.