Machine learning-based fault detection technique for bifacial PV
A UAE research team developed a hybrid 1D-CNN and random forest model to detect multiple faults in bifacial PV systems, including dust, shading, aging, and cracks. Using simulated I-V curves and a 180-day synthetic dataset, the model achieved up to 100% accuracy in general state detection and 97.6% in specific fault classification.
Mercedes unveils car with 20% efficient ultra-thin solar coating
Mercedes-Benz unveiled its first car prototype with a silicon-free, 20%-efficient nanoparticle solar coating that powers the vehicle even when off and uses modules thinner than a human hair.
Optimizing solar-plus-storage operation for markets with imbalance penalties
Scientists in Japan have used a deep reinforcement learning–based AI model to calculate discrepancies between the planned and actual electricity supply volumes in PV-battery systems operating in markets where grid imbalances are penalized. Through a series of simulations, they found that the proposed methodology can reduce imbalance penalties by approximately 47%.
Deployable tracker-based rooftop PV system for stadiums
An international research team has developed a tracker-based rooftop PV system that can be installed on both new and existing stadiums. The proposed design reportedly allows for easier deployment and delivers higher power output compared to conventional stadium PV covers.
PV module recycling gains momentum as waste volumes surge globally
A comprehensive new report from IEA PVPS Task 12 reveals how countries around the world are managing the growing volumes of end-of-life solar modules, implementing regulations and scaling recycling infrastructure to handle the expected increment in PV waste over the coming decades.
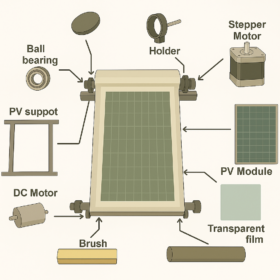
Solar panel cleaning based on rolling film, motors
Scientists in Morocco have developed a novel solar panel cleaning system designed to remove dust and bird droppings. Their prototype was built at a total cost of $386 and is ready to incorporate AI features in the future.
Supermarket EV chargers in Berlin could improve efficiency by over 250%
German researchers say shared-use and digital brokerage models could lift utilization and profitability of supermarket EV charging stations by up to 255%.
Cadmium telluride vs. crystalline silicon in agrivoltaics
Canadian researchers investigated how the transparency of cadmium telluride and crystalline silicon solar panels affects lettuce growth in agrivoltaic systems. They found that 69%–transparent silicon panels increased lettuce yield by 3.6%, whereas cadmium telluride panels led to a reduction in yield.
Novel swapping technique for partially shaded PV systems
Researchers in India have developed an algorithm for quadrant swapping in PV arrays, enabling the creation of new quadrants containing either shaded or unshaded modules. The method was tested across ten shading scenarios with varying irradiation levels and demonstrated “superior” performance compared to conventional approaches.
Sofab Inks achieves 22.2% efficiency in mini inverted perovskite solar panel
The U.S. startup said the 30 x 30 cm perovskite solar cell device featured its tin oxide electron transport material produced in a sheet-to-sheet slot die coating process.