German project for fast industrial implementation of sodium-ion battery technology
Cheap, safe, widely available sodium could be used for battery energy storage alongside photovoltaics. The Sodium-Ion-Battery Germany (SIB:DE) Research project is investigating whether sodium-ion technology can be affordably integrated into lithium-ion battery production facilities.
Sodium-ion batteries face uphill struggle to beat lithium-ion on cost
A new Stanford University study finds that there are several several key routes that sodium-ion battery developers can take to compete on price, specifically against a low-cost variant of the lithium-ion battery known as lithium iron phosphate (LFP).
Sodium-ion batteries key for India’s storage manufacturing ambitions
A new report says sodium-ion batteries (SIBs), made from abundant materials, could help India to reduce its dependence on imports to meet its energy storage needs.
German initiative to develop scalable sodium-ion batteries
A collaborative project led by German battery supplier Varta aims to develop industrial-scale sodium-ion battery technology. The final product of the three-year, €7.5 million ($8.08 million) project will be a small series of round cells for electric vehicles and stationary storage systems.
Dutch solid-state battery maker acquires factory in Scotland
Dutch startup LionVolt has acquired AMTE Power’s battery cell production line in Scotland. It says it will use the assets for pilot production of its 3D solid-state thin-film batteries.
The case for hard carbon-based sodium-ion batteries
Researchers in China have summarized the technical issues hindering the development of hard carbon, which is regarded as the most promising anode for high-performance, commercial sodium-ion batteries.
Weekend Read: Dawn of the store-age
Last year was another landmark 12 months for energy storage, with all indicators pointing to a massive surge in demand. Supply chain instability and inflation saw battery prices rise but the industry demonstrated an ability to swiftly react to geopolitical developments. We look at five trends driving the market.
Ultra-fast synthesis of nanocomposites for sodium ion batteries, supercapacitors
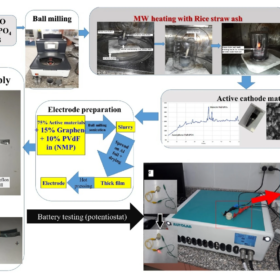
Researchers in Egypt have developed a synthesis method that uses the high microwave absorbance of silicon carbide content in rice straw ash and takes just 60 seconds to produce sodium iron phosphates-carbon nanocomposites (NaFePO4-C), which can be used as sodium ion battery cathodes and as symmetric supercapacitors.
Micro-engineered, high-performing anode for sodium-ion batteries
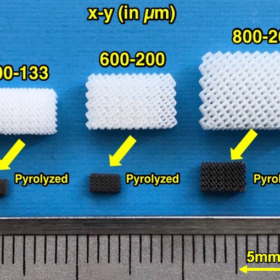
Scientists in Japan have demonstrated sodium-ion batteries using hard carbon microlattices, produced with an inexpensive 3D printer. In addition to reducing the battery size and slashing manufacturing costs, the resulting anode allows fast transportation of energy-generating ions.
Sodium-ion batteries for EVs, renewables storage
US scientist have developed a new electrolyte design for sodium-ion batteries to improve their long cycling performance. The low-solvation electrolyte was designed for high-voltage sodium-ion batteries, which retained 90% of their capacity after 300 cycles.