The Hydrogen Stream: Hydrogen-powered trains for the German network
Elsewhere, the Danish government announced a plan to deploy up to 6 GW of electrolyzer capacity by 2030 and Germany and Norway agreed to conduct a feasibility study on large-scale hydrogen transport, including via pipeline.
Symmetric redox flow battery based on Blatter radicals
A Dutch-Danish research group has provided a proof of concept for the use of Blatter radicals in electrochemical energy-storage applications. It tested these compounds in a small electrochemical cell that was found to remain stable over 275 charge/discharge cycles.
Concentrating solar power with heat storage could compete with batteries
For short-term storage in a 100% renewables grid, thermal energy storage located at concentrating solar power plants could compete with batteries, according to a new study using an idealized grid model. Seasonal storage needs could best be met with power-to-gas-to-power technology.
Storing renewable electricity with supercritical CO2 heat pump
Researchers in Spain have designed a pumped thermal energy storage system that uses supercritical carbon dioxide as a heat pump and a heat engine. The proposed system is claimed to achieve an efficiency of 80.26% and an LCOS of €0.116/kWh.
Australian electrolyzer invention enables green hydrogen under US$1.5/kg by ‘mid 2020s’
“We’re not talking about incremental improvement, this is a really giant leap,” Hysata CEO Paul Barrett told pv magazine Australia. Hysata is commercializing a breakthrough made at the University of Wollongong which effectively, Barrett says, invented a “brand new category of electrolyzer,” vastly improving efficiency.
Italian solar park to be linked to 5MW/10MWh of second-life batteries
A unit of Enel plans to deploy 5MW/10MWh of second-life batteries at Rome-Fiumicino International Airport, where a 30MW solar park is now under development. The modular storage system will include different second-life lithium-ion batteries, mainly based on nickel, manganese and cobalt chemistry, with usable storage capacity ranging from 10kWh to 25kWh.
Czechia allocates $177m for solar rebates
The funds were taken from the country’s National Recovery Plan in an effort to reduce energy dependence on Russia. A call to select eligible projects will be launched on March 22. Solar-plus-storage projects will also be entitled to participate.
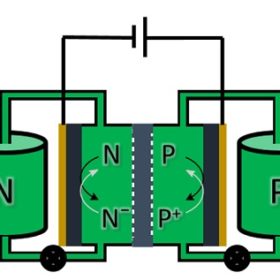
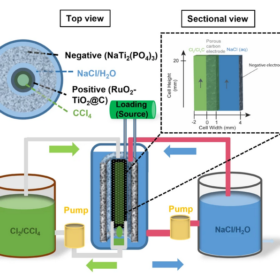
Membrane-free chlorine redox flow battery for stationary storage
A US-Chinese research group has developed a full chlorine membrane-free redox flow battery that is claimed to achieve a round-trip energy efficiency of 91% at 10 mA/cm2 and an energy density of 125.7 Wh/L. The device is based on an aqueous electrolyte made of sodium chloride (NaCl) which uses chlorine (Cl2/Cl−) redox couple as the active material for the positive electrode.
Rotation heat pump for industrial applications
Austrian tech company ecop has developed a rotation heat pump with a reported coefficient of performance (COP) of 4.0 – 7.0. The 700 kW machine operates under temperatures of 150 degrees Celsius and is based on an anticlockwise running Joule process, during which there is no phase transition of the working medium that always remains gaseous.
World’s biggest solar-plus-battery project gets funding boost
Sun Cable’s ambitious plans to build the world’s largest solar PV and battery energy storage project in Australia’s remote far north are a step closer to fruition after two of the nation’s richest men provided support for a AUD 210 million ($152.2 million) capital raise.