NREL researchers quantify UV-induced degradation levels in TOPCon solar cells
Researchers at NREL found that UV exposure can cause significant, partly non-recoverable degradation in TOPCon solar cells, with strong cell-to-cell and intra-cell variability linked to passivation and processing inconsistencies. While some UV-related losses recover quickly under light and are unlikely to affect field performance, the findings highlight gaps in current qualification tests and the need for improved UV aging standards.
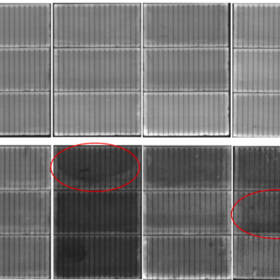
UNSW researchers identify new damp heat-induced failure mechanism in TOPCon solar modules
UNSW researchers identified a new damp-heat degradation mechanism in TOPCon modules with laser-fired contacts, driven primarily by rear-side recombination and open-circuit voltage loss rather than series-resistance increase. The study highlights that magnesium in white EVA encapsulants accelerates degradation, guiding improved encapsulant and backsheet selection for more reliable modules in humid environments.
Localized polysilicon thinning improves TOPCon solar cell performance
UNSW researchers boosted TOPCon solar cell efficiency by locally thinning the rear poly-Si layer, reducing parasitic absorption while preserving wafer integrity. The champion cell built with this approach achieved 25.10% efficiency with improved bifaciality and maintained strong passivation.
Thicker alumunium oxide layers can reduce ultraviolet-induced degradation in TOPCon solar cells
UNSW researchers developed an experimentally validated model linking UV-induced degradation in TOPCon solar cells to hydrogen transport, charge trapping, and permanent structural changes in the passivation stack. They show that thicker aluminum oxide layers significantly improve UV resilience by limiting hydrogen migration, offering clear guidance for more robust TOPCon designs.
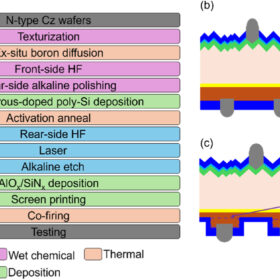
The impact of laser-assisted firing on TOPCon solar cell performance
UNSW and Jolywood studied the thermal stability of laser-assisted fired TOPCon solar cells during module fabrication and high-temperature stress, identifying hydrogen-related defect dynamics as the key factor behind degradation and recovery. They found lamination causes temporary efficiency losses that self-recover under light exposure, while optimized LAF can restore degraded contacts, providing practical guidance for reliable module manufacturing and testing.
JinkoSolar achieves world record efficiency of 27.79% for TOPCon solar cell
The Chinese manufacturer says Germany’s Institute for Solar Energy Research Hamelin (ISFH) has independently verified the result.
Toyo strikes solar cell supply deal with Voltec Solar
Japanese TOPCon specialists Toyo will become the official solar cell supplier of French solar panel manufacturer Voltec Solar, following the signing of a strategic partnership that marks Toyo’s first entry into the European market.
The impact of soldering flux on TOPCon solar cell degradation
UNSW researchers have investigated the impact of two types of soldering fluxes on TOPCon solar modules under damp heat conditions and have found that “no-clean” soldering fluxes can cause severe corrosion of front silver-aluminum contacts. The researchers have also found that denser metallisation structures and lower aluminium content improve corrosion resistance.
New research warns of unexpected UV-induced degradation in TOPCon solar cells from invisible light
Researchers from UNSW have found that invisible light accelerates UV-induced degradation in TOPCon solar cells, producing the same degradation effects as visible light but at a much faster rate. This can lead to significant open-circuit voltage losses and reduce cell efficiency.
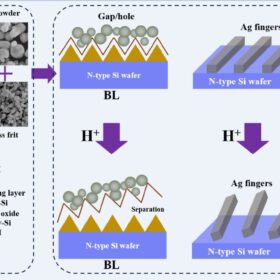
Improving LECO-compatible silver pastes to ensure TOPCon reliabilty
Researchers in China have created new silver pastes for TOPCon solar cell LECO manufacturing. The new pastes integrate either aluminum, gallium or iron and can reportedly keep cells’ electrodes securely anchored to the silicon cell surface due to the enhanced stability of the lead oxide (PbO) component in the glass powder.