Complementary hybrid PV systems can reduce reliance on storage
Looking back over years of research into the topic of hybrid systems based on different combinations of solar, wind, hydro and other renewables, an international group of scientists found strong potential for strategies to exploit complementarity between the different sources integrate more intermittent renewables onto regional and national grids. The scientists present a series of conclusions and recommendations that aim to push research in hybrid renewables forward.
Poland allocates 800 MW of solar in mixed PV-wind auction
Overall, the Polish energy regulator has allocated 1.7 GW of renewable energy capacity in a procurement exercise that was open to projects exceeding 1 MW in size. The auction concluded with a lowest price of $0.051/kWh, slightly up from the auction of the same kind held last year.
Spain to hold 3 GW renewables auction on January 26
Through the procurement exercise, the Spanish government wants to allocate 1 GW of PV, 1 GW of wind and another gigawatt of renewable energy capacity with storage.
Offshore floating PV may reach maturity in 2030
According to a report from DNV GL, the North Sea may host around 100 MW of floating solar capacity by 2030, and 500 MW by 2035. The LCOE of offshore PV systems is currently estimated at around €354/MWh but in the future it should be close to that of ground-mounted solar parks.
‘Nuclear power is now the most expensive form of generation, except for gas peaking plants’
The latest edition of the World Nuclear Industry Status Report indicates the stagnation of the sector continues. Just 2.4 GW of net new nuclear generation capacity came online last year, compared to 98 GW of solar. The world’s operational nuclear power capacity had declined by 2.1%, to 362 GW, at the end of June.
Germany launches 650 MW tender for ‘innovative’ renewables
The long-awaited procurement exercise includes 250 MW of generation capacity originally intended to be tendered last year.
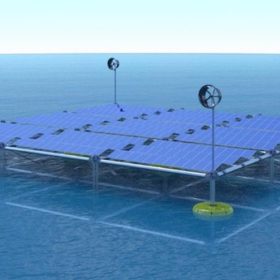
Solar arrays on wave energy generators, along with wind turbines
German startup Sinn Power has combined wave, wind and solar power to create what it claims is the world’s “first floating ocean hybrid platform.”
Denmark bets on green hydrogen
The Danish government has agreed to provide $19 million in funds for two large-scale hydrogen projects under development on the Jutland peninsula. The two projects will produce green hydrogen for the transport sector from renewables sources. Denmark’s largest energy company, Ørsted, has also announced plans for an ambitious 2 MW electrolysis plant with appurtenant hydrogen storage.
Poland’s auction for 1 MW-plus renewables projects concludes with lowest bid of $0.04248/kWh
Wind took the largest share of the awarded capacity, according to the preliminary results, but newly introduced limitations for such projects helped solar to take a significant portion of the allocated power for the first time in a Polish energy auction, with the highest bid coming in at $0.0608/kWh.
Scottish Power enters PV business
The distribution network operator for central and southern Scotland says it wants to maximize onshore renewables potential by adding solar and storage to its clean energy business. The company said hybrid projects combining wind, solar and storage will become the industry standard in 2021.