From pv magazine USA
Grid-scale storage has set another record quarter for deployment, with 4.7 GWh of installations in the third quarter, building on the previous record of 4.6 GWh set in the first quarter of 2021, according to Wood Mackenzie. This is enough battery storage to power 150,000 homes a day.
“Demand in the grid-scale and residential storage segments continues to increase, despite rising costs and lingering supply chain challenges,” said Vanessa Witte, a senior analyst on Wood Mackenzie’s energy storage team.
The market is highly consolidated for grid-scale storage, with 96% of total capacity this quarter installed in California and Texas, which are also the largest markets for utility-scale solar. Front-of-the-meter grid-scale storage is more highly concentrated in these markets than behind-the-meter residential energy storage.
“California’s reliance on energy storage to meet record peak demand this September shows why it’s absolutely critical that policymakers and grid operators remove barriers to supply to ensure reliability,” said Jason Burwen, vice president of energy storage for the American Clean Power Association.
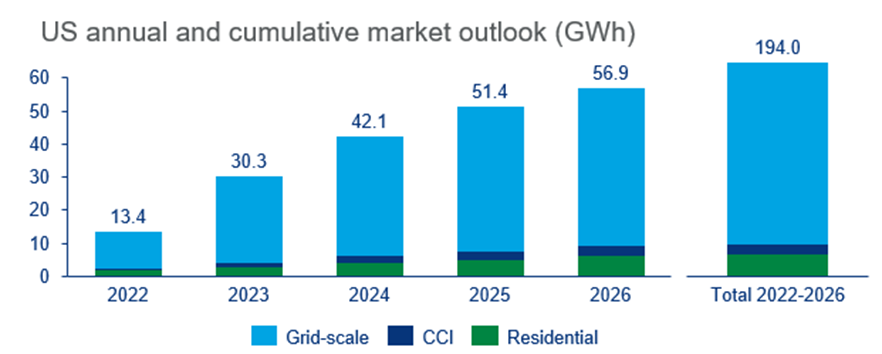
Forecasts for 2022 to 2026 increased by 109% quarter over quarter, with the US market expecting nearly 65 GW over this period. Grid-scale installations are expected to account for 84% of that capacity.
“Installed capacity is expected to more than double next year, driven by new grid-scale project announcements and increased residential and non-residential volumes in CA due to the introduction of a community solar program and NEM 3.0,” said Witte.
Popular content
Residential energy storage enjoyed a record quarter as well, with 400 MWh installed, surpassing the previous record of 375 MWh from the second quarter of 2022. California, Puerto Rico, Hawaii, and Texas led the market. Wood Mackenzie expects^ this segment to grow to 2.2 GW in 2026.
Meanwhile, community, commercial, and industrial storage had another quarter below expectations, with 56.6 MWh installed in the third quarter. Wood Mackenzie said it expects this segment to grow as well, benefiting from demand in the residential and grid-scale segments.
The trend of project delays due to supply chain constraints continues to hamper development in the near term, but 2022-28 interconnection queues have increased 120% quarter over quarter.
“Some developers have considered delaying projects into 2023 to receive tax credits from the Inflation Reduction Act, but this only applies to a very niche segment of projects,” said Witte.
Witte said supply chain issues and interconnection queue backlogs may push project installations ahead in the forecast. Due to this, Wood Mackenzie has bumped up 2024-2026 projections by 9% to 13% per year.
To continue reading, please visit our pv magazine USA website.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.


2 comments
By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.