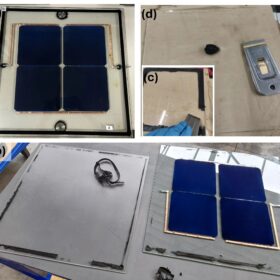
Study finds much lower-than-expected degradation in 1980s and 1990s solar modules
Researchers at SUPSI found that six Swiss PV systems installed in the late 1980s and early 1990s show exceptionally low degradation rates of just 0.16% to 0.24% per year after more than 30 years of operation. The study shows that thermal stress, ventilation, and material design play a greater role in long-term module reliability than altitude or irradiance alone.
Dutch utility testing ‘silent’ residential heat pumps
Dutch utility Eneco is testing low-noise air-to-water heat pumps from startup Whspr in around 20 homes, aiming to ease installation constraints near property boundaries. The systems reportedly achieve coefficients of performance of up to 5 and show up to 80% noise reduction in laboratory testing.
Envision claims AI-enabled storage systems can detect battery safety risks days in advance
Envision Energy has launched a fully integrated energy storage solution combining hardware, software, and market-facing AI to optimize performance, safety, and trading. Its “Physical AI” platform embeds intelligence across cells, systems, and operations, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time market participation.
Silver price surge shows no signs of slowing, hitting a new all-time high of $117.66 per ounce
Silver hit a new all-time high of $117.66/oz, climbing over 40% in the past month and 275% in the past year, driven by dollar weakness, geopolitical tensions, and gold’s strong momentum. Silver analyst Matthew Piggott tells pv magazine the metal may reach $130/oz within a couple of weeks.
Korean scientists build mini perovskite solar module with 22.56% efficiency
GIST researchers have developed a perovskite mini-module with 22.56% efficiency by improving the SnO₂ electron transport layer with PEI, reducing defects and electron loss. The module retained 94% of its performance after 500 hours, highlighting potential for scalable, stable perovskite solar cells and modules.
Sodium-ion batteries now competitive in niche markets
Sodium‑ion batteries are emerging as a safer, lower-cost alternative to lithium‑ion, with a recent international study highlighting their competitiveness in stationary energy storage. The research shows that ongoing investment and supply-chain development could enable broader adoption within the next decade.
Fraunhofer ISE developing world’s first medium-voltage solar plants
Germany’s Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (Fraunhofer ISE) is developing the world’s first medium-voltage PV plants in Germany to cut material use, reduce costs, and simplify grid integration. They will test 1,500 V and 3 kV string configurations to create cost-effective, voltage-resistant components for large-scale solar.
Analysts warn of possible, sudden silver price fall
pv magazine has spoken with silver analysts from Bloomberg and StoneX about the vertiginous growth of silver prices in recent weeks. They both agree that when prices rise too fast, investors’ behavior may change quickly. Meanwhile, the price of the precious metal has reached another all-time high today at $110 per ounce.
TU Delft unveils liquid solar module encapsulation tech
TU Delft researchers have developed a liquid-based solar module encapsulation that performs on par with conventional EVA panels while offering improved recyclability and circularity. The approach is compatible with silicon and tandem perovskite/silicon cells and could support thermal management and integration into photovoltaic-thermal modules.
China PV module prices expected to hit $0.12/W in H2
China’s PV module prices are expected to hover around $0.12/W in the second half of 2026 as the removal of export VAT rebates, front-loaded demand, and persistent oversupply keep market sentiment volatile.