Photovoltaics for agromining
Researchers in France have investigated how photovoltaic power generation can be combined with the growth of hyperaccumulating plants in disused, contaminated brownfield land and have found this combination could help increase the profitability of the so-called agromining – a plant-based approach to cleaning up contaminated environments.
How albedo interacts with different rooftop PV system patterns
Researchers have simulated 160 cases of PV rooftop installation in southern and northern Italy. Among changing parameters were size and type of the panels, as well as their roof cover rate. The considered albedos were 20%, 40%, 60%, and 80%, representing different types of roof materials.
CNNP Optoelectronics unveils 16.5%-efficient perovskite solar module
CNNP Optoelectronics has started producing a 1,200 mm × 1,600 mm perovskite solar module on a 200 MW pilot line, marking a step toward scaling commercial manufacturing of next-generation PV technologies.
Premier Energies commissions 1.2 GW TOPCon solar cell line
The new line increases Premier Energies’ solar cell capacity from 2 GW to 3.2 GW. The Indian manufacturer is on track to scale this up to 8.4 GW by June 2026.
Sierra Space adds production capacity for solar power systems for satellites
The U.S.-based commercial aerospace and defense technology company, announced a new $45 million facility in Colorado to manufacture solar array systems to serve the growing satellite market.
Tonalli solar panel factory inaugurated in Mexico with capacity to produce 200,000 units a year
The new plant, located in Puebla, aims to supply solar energy to schools, rural communities and the agricultural sector, with an investment of more than MXN 325 million and the generation of more than a thousand jobs.
Wafer producers scramble to stay afloat despite hydropower advantage
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, OPIS, a Dow Jones company, reports that FOB China wafer prices remained stable this week amid weak demand and low production. It says manufacturers continue to face margin pressure despite seasonal hydropower cost relief and traceability documentation premiums.
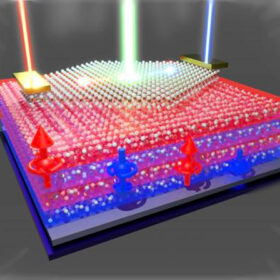
New device could pave way for magnetic controllable photovoltaic devices
Scientists in Japan have developed a device that enables external magnetic field control of magnetic injection current in the bulk photovoltaic effect (BPVE), a phenomenon not yet used in commercial solar cells. The research suggests a potential path toward regulating photocurrent in next-generation photovoltaic applications.
Photovoltaics vs. photovoltaic-thermal
Researchers in India say that photovoltaic-thermal (PVT) systems offer greater performance stability than conventional PV systems in hot climates. Using irradiance and temperature data, the team applied a Random Forest model that predicted efficiency classes with 97% accuracy.
Premier Energies commissions 1.2 GW TOPCon solar cell line in India
Premier Energies has commissioned a 1.2 GW tunnel oxide passivated contact (TOPCon) solar cell line at Fab City in Hyderabad, India, increasing its total cell manufacturing capacity to 3.2 GW.