Tesla’s storage facility comes online at Mohammed bin Rashid solar park in Dubai
The 1.21 MW/8.61 MWh storage facility is the second battery deployed at the 5 GW solar park. The system allows bi-directional charging.
Delta expands string inverter series with two new products
The two three-phase inverters feature two maximum power point trackers and have input voltages ranging between 200 and 1,000 V DC. The smallest device has an efficiency of 98.3% and the largest 98.5%.
Residential lithium-ion battery from Belgium
The battery is available in three versions, with storage capacities of 3 kWh, 5 kWh and 7 kWh with all devices featuring a nominal voltage of 51.2 V and a maximum charging voltage of 56.8 V.
Australian research shows tandem cells should follow PERC for multi-TW production
A new paper from the University of New South Wales underscores the urgent global need for tens of terawatts of PV to replace fossil fuels by 2050. The researchers say it’s time to focus on the most sustainable technologies, before reserves of silver, indium and bismuth dry up.
Work starts on 80 MW behind-the-meter solar project in the US
The array will supply energy to a steel mill in Texas and is expected to reach commercial operation by the summer of 2023.
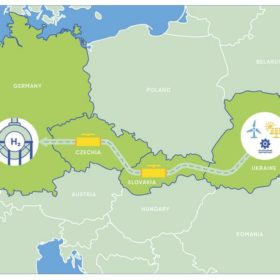
The Hydrogen Stream: Hydrogen highway through Central Europe
Elsewhere, the German government wants to allow the testing of hydrogen production from offshore electricity, while a French consortium intends to promote the use of hydrogen at airports and build a European airport network to accommodate future hydrogen aircraft. Furthermore, the Port of Rotterdam is increasing its efforts to become a hydrogen hub.
Interface engineering for a stable, 23.4% efficient perovskite solar cell
Scientists led by Switzerland’s École Polytechnique Fedérale de Lausanne (EPFL) demonstrated a simple approach to designing the interface between two layers in a perovskite solar cell, which was shown to improve both the performance and stability of the device. Solar cells fabricated by the group achieved 23.4% conversion efficiency, and were operated for close to 6,000 hours before degrading beyond 80% of this initial value.
Chinese PV Industry Brief: Rising solar glass prices and a major polysilicon supply deal
Shuangliang Eco-Energy has agreed to buy a total of 134,950 MT of polysilicon from two different manufacturers. Furthermore, the Chint group said it wants to deploy another 3 GW of rooftop solar and PV InfoLinks reported on rising glass prices.
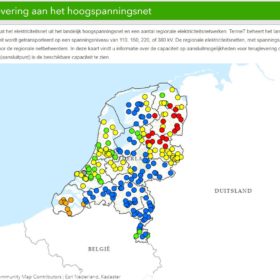
Dutch transmission system operator releases online map showing available grid capacity
The interactive map gives solar and wind project developers, as well as regional grid operators direct insight into where and how much capacity is available at Tennet’s high-voltage stations.
Canal in Spain may host 160 MW solar plant
The government of Spain’s Navarra region has approved a 160 MW solar project planned by the local renewable energy association Anpier. The plant is to be deployed on the Canal of Navarra, which is one of the country’s largest artificial irrigation canals.