France approves new climate law, including several measures to support PV
The Climate and Resilience Law was officially promulgated and published in the official journal on August 24. For solar, several measures could have a direct impact on the development of projects in the years to come.
Heat pump control strategy for solar assisted district heating
Researchers in Spain have proposed two control strategies for the integration of heat pumps in district heating systems assisted by solar thermal collectors. Their technical-economic analysis shows that the proposed combination can reduce reliance on gas while also reducing costs.
Brazil hits 10 GW milestone
Around 2 GW of new PV capacity were deployed in the Latin American country over the past five months.
Chinese PV Industry Brief: Shandong province wants to deploy another 35 GW of PV over the next five years
In addition, JA Solar was able to ship 10 GW of modules in the first six months of the year and raise RMB5 billion for new production capacity.
Public debate begins on France’s largest solar-plus-storage project
The 1 GW Horizeo project includes a solar plant, battery storage, a green hydrogen production unit, a data center, and an agrivoltaic facility. It is being planned near Saucats, a municipality in the Gironde department in Nouvelle-Aquitaine in southwestern France.
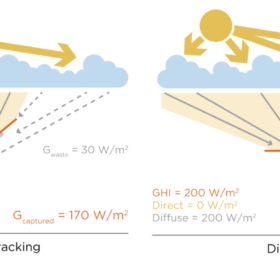
TÜV Rheinland confirms that Soltec’s algorithm increases PV plant yields by 5.3% on cloudy days
TÜV Rheinland has verified the performance of the Soltec Diffuse Booster algorithm, which uses both sensors and weather forecasts to drive its solar trackers. According to the manufacturer, it can increase the annual revenue of a 100 MW PV plant in Spain by €1.8 million.
Bullish clean energy stocks helped maintain healthy investment levels
The latest renewables investment report produced by analyst BloombergNEF has noted backing for solar projects continued to rise in the first half as wind power investment fell back.
Mini perovskite solar module with 19.2% efficiency via new additive
The efficiency of the module was certified by the U.S.’ National Renewable Energy Laboratory. It was built with perovskite solar cells with a stabilized efficiency of 23.6%, an open-circuit voltage of 1.17 V, a short-circuit current density of 24.1 mA per cm−2, and a fill factor of 0.842.
Indian solar developer to build 3.5 GW green hydrogen project in Oman
Acme Solar said the facility would use 3 GWp of solar and 0.5 GWp of wind energy to produce 2,400 tons of green ammonia daily and approximately 900,000 tons annually. Construction is planned in phases with an investment of $3.5 billion over the next three years.
Green roof improves solar panel efficiency by 3.6% on average
The comparison of two solar cladded roofs in Sydney, Australia, one bare beneath its panels and the other adorned with native grasses and plants, has found the panels on the green roof were, on average, 3.63% more efficient, producing an average daily output 13% greater than the conventional roof. The improvements are believed to stem from the lower temperatures on the green roof, thanks to its plants – which also provided a plethora of additional benefits.