The Hydrogen Stream: Asahi Kasei to test alkaline water electrolyzer
Japan’s Asahi Kasei is testing a new alkaline water electrolyzer, while China has started developing its first 100 kg vehicle-mounted liquid hydrogen system.
Key takeaways from World Hydrogen 2024 in Rotterdam
Development of green hydrogen production in Europe is moving forward in fits and starts, but the ongoing World Hydrogen 2024 event in Rotterdam calls for blue hydrogen adoption, which suggests that the oil and gas industry aims to maintain control of the hydrogen market.
The warming effect of PV on land surface temperature
Researchers in Japan have analyzed the warming effect of photovoltaic system on land surface temperature around the Kushida River Basin for ten years and have found this value increased by an average of 2.85 C.
SolarDuck, Tokyu Land install Japanese floating solar pilot
SolarDuck and Tokyu Land have installed a floating solar demonstration unit in Japan. This project is billed as the nation’s first offshore floating solar power plant on the surface of the ocean and will be used to power electric vehicles and boats.
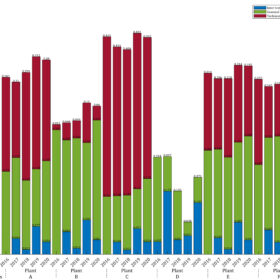
Japan allocates 1.09 GW of storage in capacity auction
The Japanese authorities selected 30 battery storage projects in the procurement exercise. The selected developers and plant owners will be awarded a 20-year fixed revenue.
The impact of seasonal, meteorological factors on PV plant performance
Scientists in Japan have investigated the impact of seasonal, metereological factors on solar plant performance and have found the average power generation inefficiency reached significant levels. The findings suggest that optimal site for power plants requires careful consideration of meteorological and geographical data.
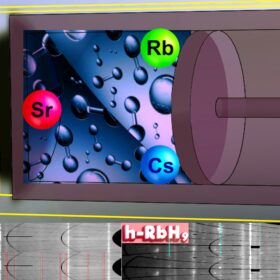
Researchers propose use of cesium, rubidium for hydrogen batteries
A study led by Russia’s Skoltech and China’s HPSTAR suggests that rubidium and cesium additives could improve the efficiency of hydrogen batteries. Researcher Dmitrii Semenok tells pv magazine that “it is a question of changing the approach to the search for promising hydrogen storage materials.”
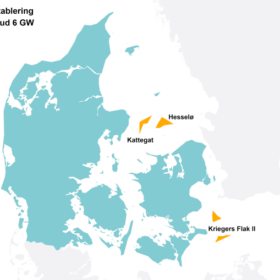
The Hydrogen Stream: Denmark may produce green hydrogen from wind
Denmark will procure at least 6 GW of offshore wind power capacity to potentially produce hydrogen, while Orlen says it will use a European Commission grant to build 16 hydrogen refueling stations in Poland.
The Hydrogen Stream: Vale opens hydrogen metallurgy lab in China
Vale and Central South University have launched a joint laboratory for low-carbon and hydrogen metallurgy in Changsha, in China’s Hunan province, while Nippon Steel has secured approval to acquire U.S. Steel.
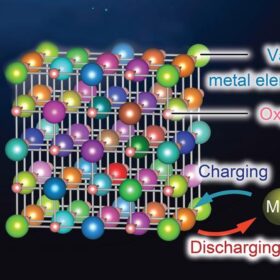
Rechargeable magnesium batteries for grid-scale storage
Researchers in Japan have developed a novel cathode material for rechargeable magnesium batteries (RMBs) in the form of rocksalt oxide. This new material reportedly enables efficient charging and discharging even at low temperatures.