Powering the AI revolution
Developers from the renewable energy and data center markets are working to find common ground to meet surging energy demand fueled by the artificial intelligence boom.
Allegro Energy unveils Australia’s first domestic microemulsion flow battery for LDES
Allegro Energy has introduced Australia’s first domestically produced microemulsion flow battery for long-duration energy storage (LDES). The company will pilot the technology with Origin Energy at the Eraring power station.
Chinese scientists build polysulfide-iodide redox flow battery with 87.9% energy efficiency
Scientists in China designed a suplhuer-based redox flow battery with a peak power density of 95.7 mW cm2 and an average energy efficiency of 76.5% at 30 mA cm2 within 50 cycles.
NHPC launches bidding for 1.2 GW of solar, 600 MW of storage in India
NHPC Ltd. has issued a tender for 1,200 MW of grid-connected solar projects with 600 MW/2.4 GWh of energy storage, offering an additional 1,200 MW under a Greenshoe option. Bidding closes on April 24.
Solar-plus-storage for extreme low temperatures
Scientists in the United States have created a testing platform for energy harvesting in solar-plus-storage systems under extreme temperatures ranging from -180 C to 300 C.
Estonia’s largest battery goes online
The flagship battery storage project commenced operations on February 1, only days before cutting ties with the Russian power grid.
Power electronics for customized battery energy storage
Startup p&e power&energy is offering multilevel inverter technology to manufacturers and integrators of battery energy storage systems (BESS). Interconnecting individual cells enables cost savings and the service life and efficiency of the systems, which can be individually configured for each application, can be increased.
Sulzer, Hyme Energy to commercialize novel molten salt energy storage
Sulzer is developing advanced pumps for Hyme Energy’s patented molten hydroxide salt energy storage technology. Building on the success of the pioneering Molten Salts Storage (MOSS) project in Denmark, the partners now seek to commercilize the solution.
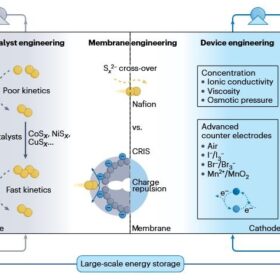
Pathway to commercialization of aqueous sulfur-based redox flow batteries
Researchers in China have identified a series of engineering strategies to bring aqueous sulfur-based redox flow batteries closer to commercial production. Improving catalyst design, ion-selective membranes, and device integration will be key to solve this battery storage technology’s issues.
Heat pump control strategy for energy communities
Researchers have utilized measured data from a small energy community on a Finnish university campus to simulate its operation under various control strategies. The first control strategy prioritizes the use of heat pumps, while the second prioritizes price. Total costs were reduced by up to 25% with the second option.