Survey highlights fire-detection, suppression issues in battery storage systems
A new Clean Energy Associates (CEA) survey shows that 26% of battery storage systems have fire-detection and fire-suppression issues, while about 18% face challenges with thermal management systems.
Offshore floating PV system based on dual-axis tracker, tension leg platform
Developed by scientists in Spain, the HelioSea system is reportedly able to ensure structural reliability in challenging marine environments. The research group proposed to use tension leg platforms that have been successfully applied to offshore drilling platforms, where stability is also paramount.
Slenergy releases residential PV system package with heat pump
Slenergy has introduced a new residential PV system package featuring 425 W solar panels, a hybrid inverter, a high-voltage battery, and a Slenergy-branded heat pump. The package incorporates Internet-of-Things hardware for real-time data collection and intelligent control strategies.
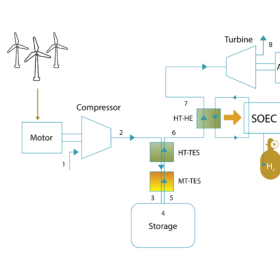
Green hydrogen, power generation tech based on compressed air storage, solid-oxide electrolysis cells
Scientists in Korea have developed a compressed air storage system that can be used as a combined cooling, heat, and power system and provide heat and power to solid-oxide electrolysis cells for hydrogen generation. It showed an overall roundtrip efficiency of 121.2% and over-unity efficiencies in the range of 100% to 120%.
French consortium unveils multi-functional solar roofing solution
A French consortium has developed a roofing solution that integrates solar, storage, rainwater management, and the protection of vegetation. The group says plants under the PV modules can increase solar power generation by more than 10%.
Australian off-grid project upgrade shows power of modern PV
An off-grid residential system on a secluded island in Australia has received a new tech upgrade. The additional capacity highlights the new era of off-grid living available to remote households in the country.
SEG Solar unveils 700 W TOPCon solar modules with 22.53% efficiency
SEG Solar says its new panels have a temperature coefficient of -0.30% per C. They come with a 30-year power output guarantee for 87.4% of the initial yield.
NREL outlines feasibility of heat pumps in US market
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has outlined the feasibility of heat pumps in the US market in a new report. It says installation costs and energy savings prices have changed in relation to climate, heating sources, and types of homes. It says policymakers should further reduce the costs of installing heat pumps to benefit more US households.
Large-format solar modules and legacy assumptions
While most large-format modules are lab tested for certification, the lab is not the real world. The field loading applied to a solar module depends on the structure on which it is mounted and the terrain of the project.
TechBlick’s event shows roadmaps for perovskite, organic PV
A recent industry event about organic, perovskite, and other emerging cell technologies hosted by TechBlick revealed advances in power conversion efficiencies, stability, availability of materials, and specialized manufacturing equipment. The event also showed that the number of startup companies, new products and new pilot lines is increasing at a fast pace.