Massive 20 GWh sodium-ion battery manufacturing plant announced in China
After last year’s slowdown, investment in China’s sodium-ion battery sector is rebounding in 2025, and one of the biggest projects yet has now entered the development pipeline.
Capture price exposes true performance of solar plants
French solar engineering firm kiloWattsol says technical assessments show that capture-price analysis provides a more accurate measure of photovoltaic asset performance than France’s monthly M0 benchmark, as price volatility and negative wholesale prices increase.
Residential installations lead Dutch storage boom
The phasing out of net-metering for solar installations is incentivizing a growing number of citizens to install residential battery storage systems in the Netherlands. Analysts are predicting the upward trend will accelerate in the coming years.
Wind-PV-powered heat pump for low-energy residential buildings
Scientists in China have developed an optimized energy management strategy for a wind-PV hybrid heat pump system that uses both thermal and electric energy storage. Using different seasonal interaction management strategies, they simulated four operational cases.
Chinese PV Industry Brief: Cybrid Technologies ships first optical conversion films for perovskite tandem solar modules
Cybrid Technologies announced the first mass delivery of optical conversion films for perovskite tandem solar modules, marking what it described as the world’s first commercial application of this technology.
Efficient solar PV cooking with sand-based thermal energy storage
Scientists in Ghana have developed a device that combines a conventional solar PV-powered steam cooker with sand-based thermal energy storage. The system can achieve a thermal efficiency of 38.9% and has a payback period of 4.5 years.
Oscal releases 2 kWh battery for home, off-grid, on-grid use
The Chinese company said its 2,016 Wh portable LiFePO₄ energy-storage system is expandable to 22,176 Wh with additional battery modules. It delivers 2,400 W output, offers 16 ports, app-based control, and includes built-in audio and lighting features for home, travel, and off-grid use.
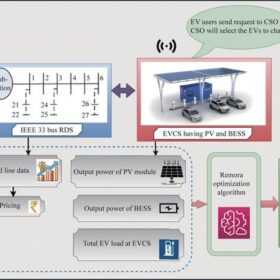
How to balance power losses, cost effectiveness in PV-BESS-driven EV charging stations
Scientists in India have developed a novel method to optimize the placement of an EV charging station on the grid, along with the size of its PV generation and battery storage. They have also created a framework for an innovative slot offering.
Paraguay set to host autonomous solar-powered data center
Sollar Machine plans to build a $9 million off-grid data center in Paraguay powered entirely by solar and batteries to deliver high-performance computing services for international clients, with a focus on AI.
Cash flow analysis shows adiabatic compressed air storage is viable for 10–100 h applications
Scientists in the United Kingdom have compiled a new database of adiabatic compressed air energy storage projects. Using this data, they were able to determine the experience rate and identify the conditions under which the technology would be economically viable. According to their findings, costs have declined at a 15% learning rate since 2013.