Low Carbon, ElectroRoute sign four PPAs covering 140 MW of UK solar
Four balancing PPAs will see ElectroRoute trade Low Carbon solar assets in UK electricity market. The agreements are set to run until 2028.
Is solar really the root cause of Spain’s massive power outage?
Some media outlets have speculated that Spain’s April 28 blackout may have been caused by a disconnected solar plant, but DNV grid analyst Andrea Mansoldo tells pv magazine that it was likely due to a combination of grid weakness and low-frequency oscillations.
Biwatt releases 4.5 kWh sodium-ion battery
The Chinese manufacturer said its new IP65-rated product has a lifetime of 5,000 cycles. Up to four batteries can be stacked together, with total storage capacity reaching 72 kWh.
Colombia approaches 2 GW solar capacity milestone
Colombia is approaching 2 GW of cumulative installed PV capacity, with 1.34 GW currently operational and an additional 700 MW in testing, according to the country’s grid operator.
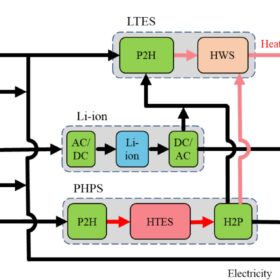
How to integrate solar-plus-storage with heat pumps
Scientists in Spain have simulated a system that uses both power-to-heat-to-power thermal batteries and lithium-ion batteries for energy storage. The hybrid system reportedly achieved a 7% lower LCOE compared to a PV system relying solely on lithium batteries, while simultaneously increasing PV self-consumption by up to 20%.
Takamiya launches vertical mounting solution for agrivoltaics, areas with little space
The Japanese company said its new vertical mounting system is ideal for farmland, regions with heavy snowfall, along factory fences, and in parking areas.
Chinese PV Industry Brief: DMEGC posts gains as peers hit by weak Q1
Chinese solar manufacturers have reported mixed first-quarter results. DMEGC recorded strong growth while peers such as HiUV, Risen, Autowell and Jolywood suffered sharp declines amid falling prices and oversupply.
Spain blackout not caused by renewables, says prime minister
Spanish Prime Minister Pedro Sánchez says Spain’s recent blackout was not triggered by excess renewables or a lack of nuclear power. He claims the government will reform the grid, seek an independent report from Brussels, and launch a national inquiry.
ZTT debuts 7.58 MWh liquid-cooled battery storage system
The Energrid NA7 incorporates ZTT’s self-developed 3S-integrated power conversion system (PCS) and supports 2000 V high-voltage DC input.
History repeats as Iberian blackout demonstrates urgent need for battery storage
The vast blackout that gripped the Iberian Peninsula on April 28 has echoes of a similar event in an Australian state in 2016. The solution in both cases appears to be the same.